Strategies in Java or Java strategies is an impressive and fashionable side of Java programming.
What are Strategies in Java?
A technique in Java is a block of code that, when referred to as, plays particular movements discussed in it. As an example, when you’ve got written directions to attract a circle within the manner, it is going to do this job. You’ll be able to insert values or parameters into strategies, and they’ll simplest be achieved when referred to as. They’re additionally known as purposes. The main makes use of of strategies in Java are:
- It permits code reusability (outline as soon as and use a couple of instances)
- You’ll be able to destroy a fancy program into smaller chunks of code
- It will increase code clarity
The way to Claim Strategies in Java?
You’ll be able to simplest create a technique inside of a category. There are a complete of six elements incorporated in a technique declaration. The elements supply more than a few details about the process.
Beneath is the syntax to claim a technique and its elements record.
public int addNumbers (int a, int b){
//manner frame
}
Get entry to specifier:
It’s used to outline the get admission to form of the process. The above syntax sees using the “public” get admission to specifier. Alternatively, Java supplies 4 other specifiers, which might be:
- Public: You’ll be able to get admission to it from any magnificence
- Non-public: You’ll be able to get admission to it inside the magnificence the place it’s explained
- Safe: Available simplest in the similar package deal or different subclasses in any other package deal
- Default: It’s the default get admission to specifier utilized by the Java compiler if we don’t point out every other specifiers. It’s obtainable simplest from the package deal the place it’s declared
ReturnType:
It defines the go back form of the process. Within the above syntax, “int” is the go back sort. We will point out void because the go back sort if the process returns no price.
Approach identify:
It’s used to provide a novel identify to the process. Within the above syntax, “addNumbers” is the process identify. This educational seems to be at some pointers for naming a technique, in a while.
Parameter record:
This can be a record of arguments (knowledge sort and variable identify) that shall be used within the manner. Within the above syntax, “int a, int b” discussed inside the parentheses is the parameter record. You’ll be able to additionally stay it clean should you don’t need to use any parameters within the manner.
Approach signature:
You don’t must do anything else further right here. The process signature is only a aggregate of the process identify and parameter record.
Approach frame:
That is the set of directions enclosed inside of curly brackets that the process will carry out.
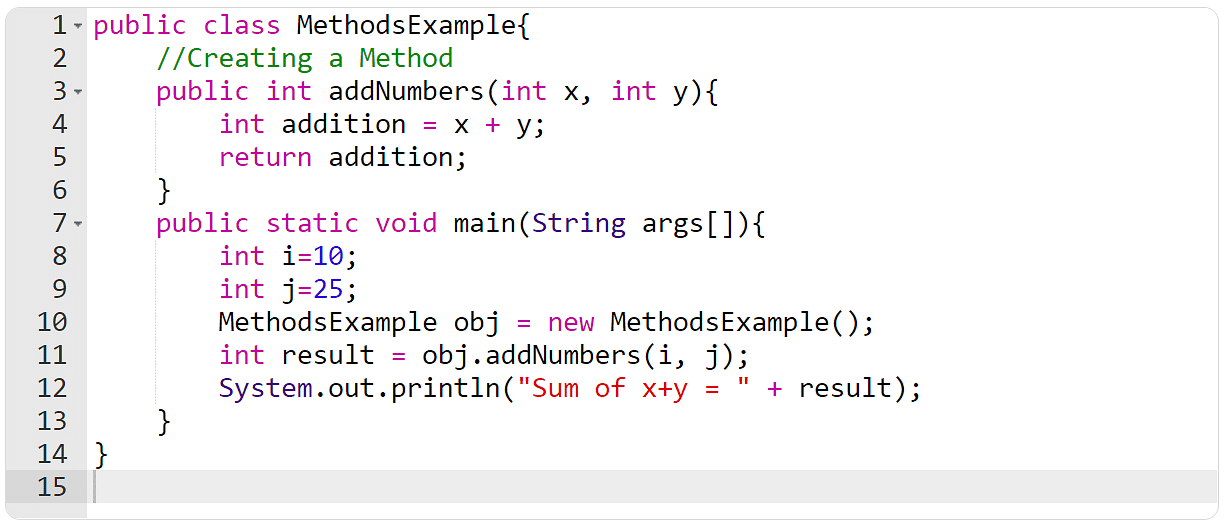

Within the above instance:
- ‘Public’ is the get admission to specifier
- The go back sort is ‘int’ (i.e. integer)
- The process identify is addNumbers
- int x and int y are the parameters
- addNumbers (int x, int y) is the process signature
- The process frame is:
{
int addition = x + y;
go back addition;
}
Including an Instance could be nice to extend the readability about the concept that
The way to Title a Approach?
One of the vital regulations and tricks to identify the strategies in Java are:
- Attempt to use a reputation that corresponds to the capability (if the process is including two numbers, use upload() or sum())
- The process identify will have to get started with a verb and in lowercase (Ex: sum(), divide(), space())
- For a multi-word identify, the primary observe will have to be a verb adopted via a noun or adjective with none area and with the primary letter capitalized (Ex: addIntegers(), areaOfSquare)
Java Approach Parameters
Java manner parameters are essential elements that permit strategies take knowledge as inputs and procedure them accordingly. Writing dependable and reusable Java code calls for figuring out the way to use and handle manner arguments.
The way to Name a Approach?
As discussed previous, you want to name a solution to execute and use its functionalities. You’ll be able to name a technique via the use of its identify adopted via the parentheses and a semicolon. Beneath is the syntax for calling a technique:
upload();
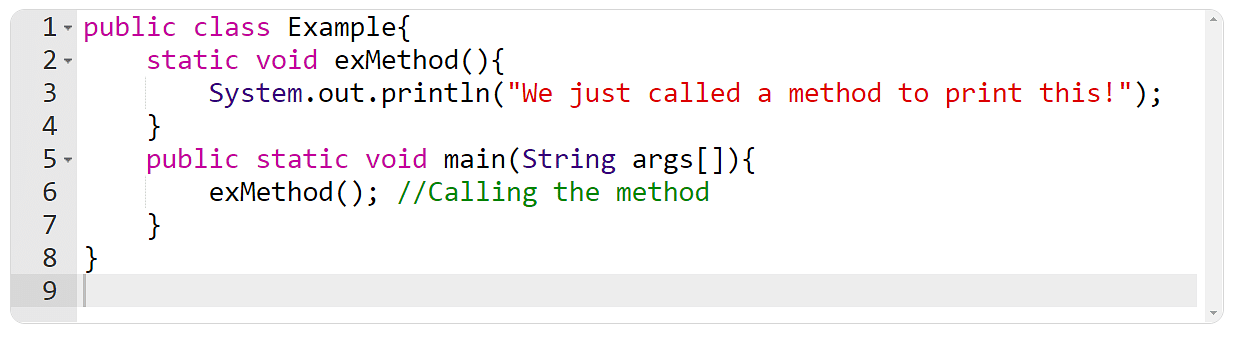
The instance underneath will create an instance manner named exMethod() and speak to it to print a textual content.

What are the Sorts of Strategies in Java?
Strategies in Java may also be widely categorized into two sorts:
Predefined Strategies
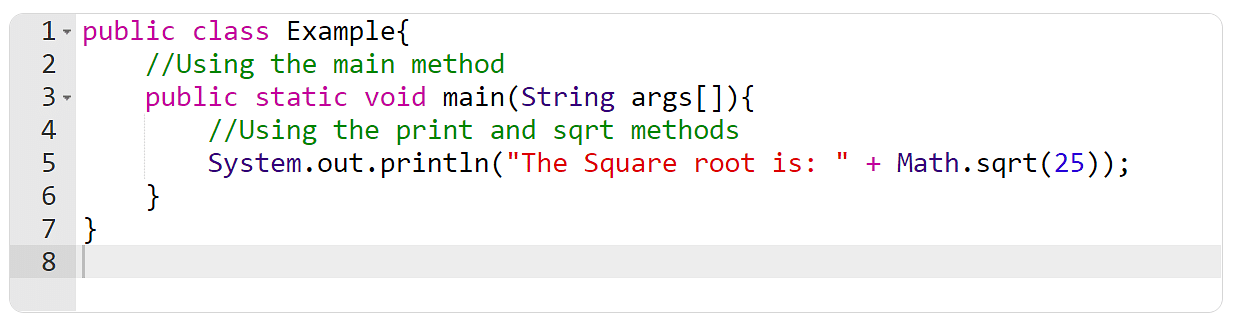
Because the identify provides it, predefined strategies in Java are those that the Java magnificence libraries already outline. Because of this they may be able to be referred to as and used anyplace in our program with out defining them. There are a lot of predefined strategies, akin to duration(), sqrt(), max(), and print(), and every of them is explained within their respective categories.
The instance discussed underneath makes use of 3 predefined strategies, which might be major(), print(), and sqrt().

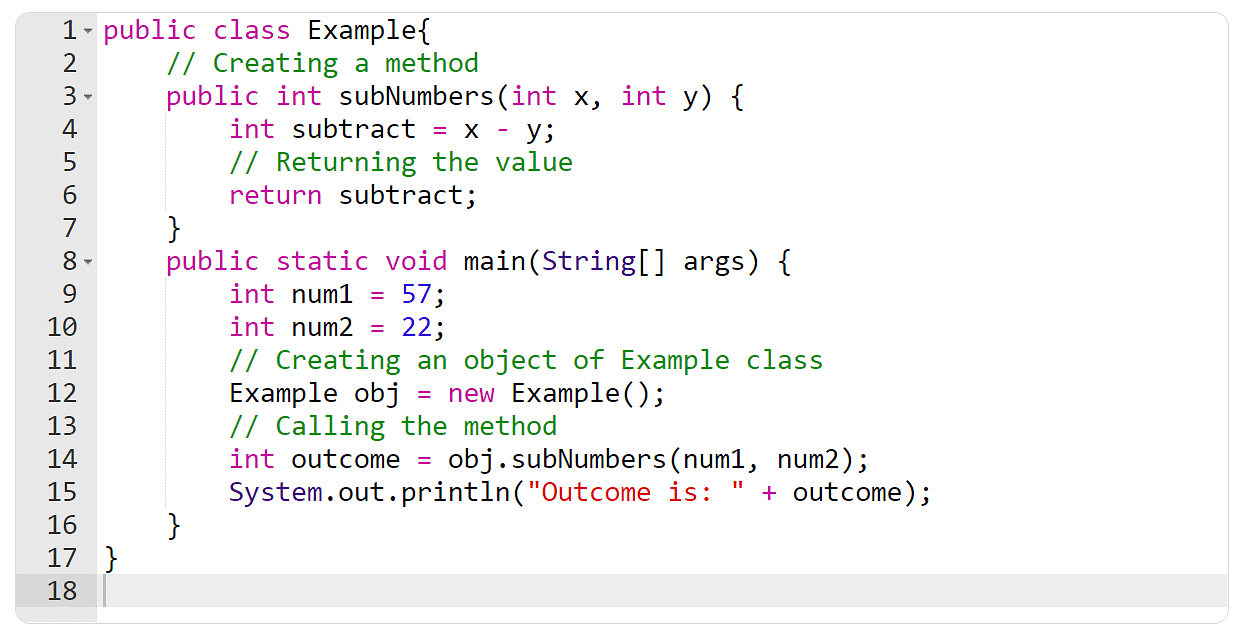
Person-defined Strategies
Customized strategies explained via the person are referred to as user-defined strategies. It’s imaginable to change and tweak those strategies in step with the location. Right here’s an instance of a user-defined manner.

Strategies in Java may also be categorized into the next sorts:
- Static Approach
- Example Approach
- Summary Approach
- Manufacturing facility Approach
Developing Static Strategies in Java
Static strategies are those that belong to a category and now not an example of a category. Therefore, there is not any want to create an object to name it, and that’s probably the most vital benefit of static strategies. It’s imaginable to create a static manner via the use of the “static” key phrase. The main manner the place the execution of the Java program starts may be static.
Please upload the code manually via typing
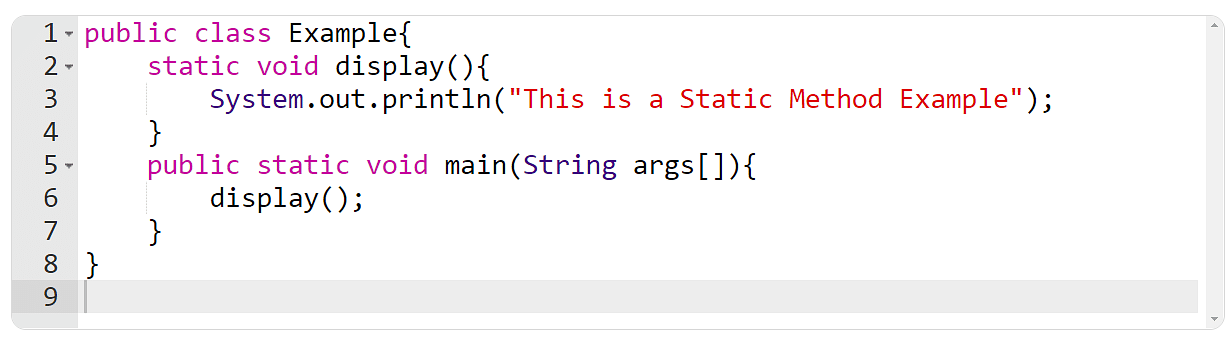

Making use of Example Strategies in Java Code
The example manner is a non-static manner that belongs to the category and its example. Developing an object is essential to name the example manner.
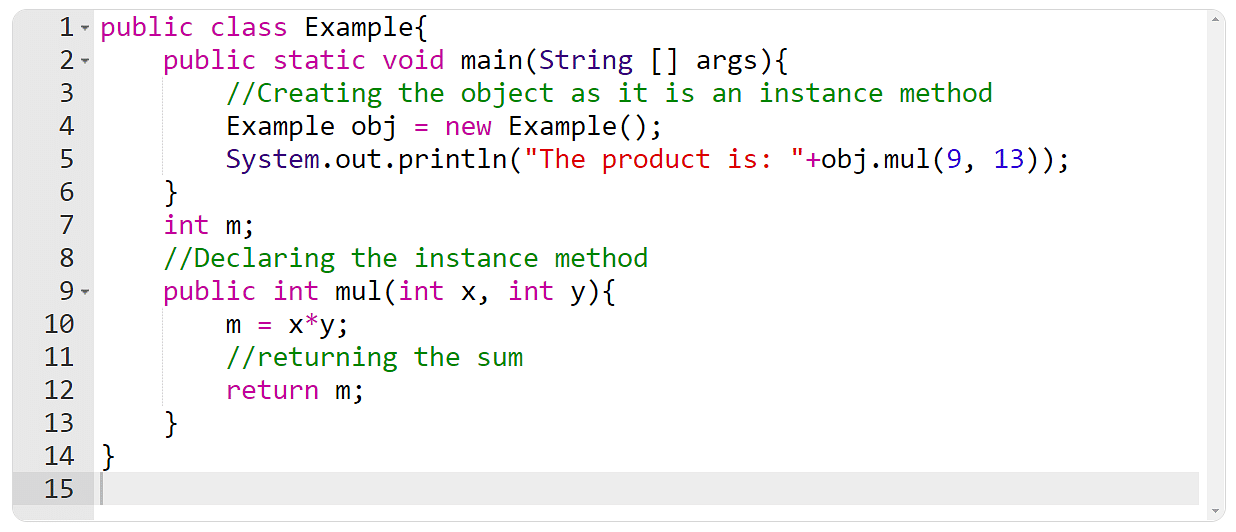

Example strategies are additional divided into two sorts:
It’s used to get a non-public box’s price, accessor strategies in Java can simplest learn example variables. They’re at all times prefixed with the observe ‘get’.
It’s used to get and set the price of a non-public box, mutator strategies in Java can learn and regulate example variables. They’re at all times prefixed with the observe ‘set’.
The use of Summary Strategies in Java
Summary strategies in Java wouldn’t have any code in them. Because of this there is not any want to give you the implementation code whilst mentioning it. As an alternative, it’s imaginable to claim the process frame later in this system. It’s recognized that one can claim an summary manner via the use of the “summary” key phrase. There’s any other exhausting rule to claim summary strategies, and it’s that they may be able to simplest be declared inside of an summary magnificence.
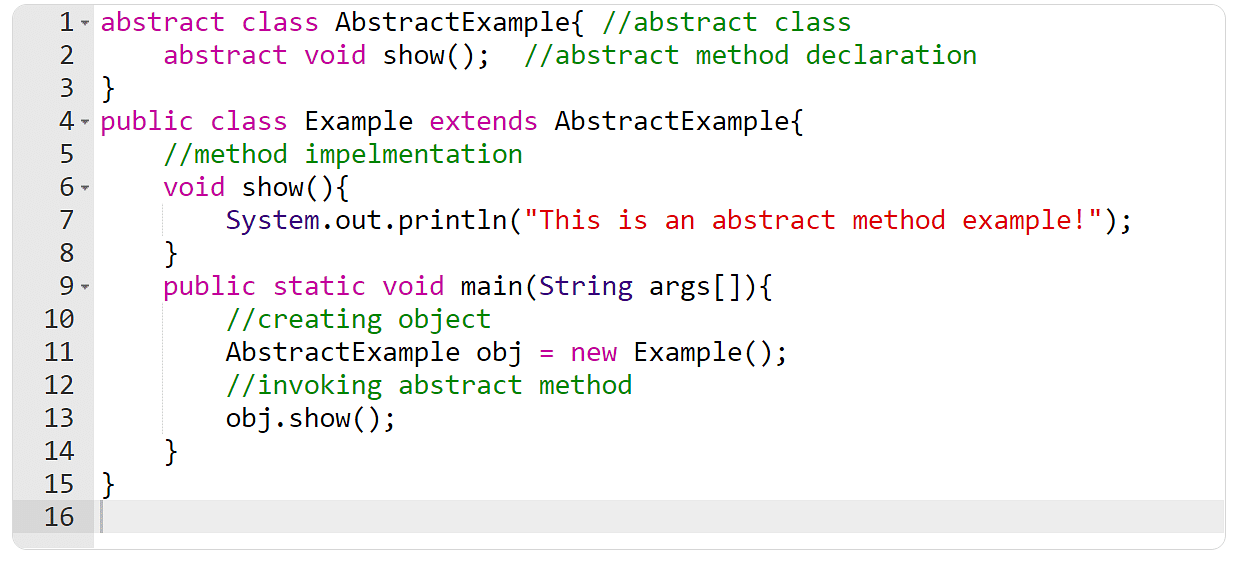

Manufacturing facility Approach
Manufacturing facility strategies are those that go back an object to the category the place it belongs. Most often, all static strategies additionally fall into this sort of manner.
Do not fail to see the chance to turn out to be a Qualified Skilled with Simplilearn’s Put up Graduate Program in Complete Stack Internet Building. Sign up Nowadays!
Sorts of Approach Parameters
1. Formal Parameters
Those arguments function stand-ins for the values equipped to the process when it is known as; they’re explained within the manner declaration. The process ‘public void greet(String identify)’ makes use of ‘identify’ for example of a proper parameter.
2. Precise Parameters
When a technique name is made, the process receives those precise values or parameters. As an example, ‘Alice’ is the real parameter within the remark ‘greet(“Alice”)’.
Parameter Passing in Java
Java passes parameters to strategies by the use of the pass-by-value mechanism. This means {that a} replica of the variable’s price is created and handed when a variable is provided to a technique. Subsequently, the unique price out of doors the process is unaffected via adjustments made to the parameter within the manner.
Primitive Knowledge Sorts
The true price is handed when sending primitive knowledge sorts (akin to int, glide, and double). The unique variable stays unchanged when changes are made to the parameter within the manner.
public magnificence Instance {
public static void major(String[] args) {
int num = 10;
modifyValue(num);
Device.out.println(num); // Output: 10
}
public static void modifyValue(int price) {
price = 20;
}
}Reference Knowledge Sorts
The reference (or deal with) to an object is handed via price when passing items. Because of this, changes made to the thing’s fields within the manner may have an affect at the supply object. Reassigning the reference may not have any affect at the authentic reference, even though.
public magnificence Instance {
public static void major(String[] args) {
Particular person particular person = new Particular person("John");
modifyPerson(particular person);
Device.out.println(particular person.getName()); // Output: Mike
}
public static void modifyPerson(Particular person p) {
p.setName("Mike");
}
}
magnificence Particular person {
non-public String identify;
public Particular person(String identify) {
this.identify = identify;
}
public String getName() {
go back identify;
}
public void setName(String identify) {
this.identify = identify;
}
}Varargs (Variable Arguments)
Java’s varargs (variable arguments) permit how you can take any collection of parameters. That is useful if you find yourself undecided of the appropriate amount of arguments that shall be equipped to the process.
Syntax
3 dots (…) claim the varargs parameter. It must be the remaining parameter within the record of parameters for the process.
public static void printNumbers(int... numbers) {
for (int num : numbers) {
Device.out.println(num);
}
}
public static void major(String[] args) {
printNumbers(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // Output: 1 2 3 4 5
}The use of those concepts, Java programmers can design adaptable, sensible strategies and take care of more than a few enter parameter sorts. This figuring out is the root for growing a hit Java apps.
Java Approach Overloading
Java manner overloading permits many strategies with the similar identify inside of a category so long as their argument lists range. That is a demonstration of Java’s polymorphism, which permits a unmarried manner identify to hold out many purposes relying on its arguments.
Key Ideas of Approach Overloading
1. Approach Signature
- Approach overloading is decided via the process signature, which contains the process identify and the parameter record. The go back sort isn’t thought to be when overloading strategies.
- Two strategies are thought to be overloaded if they have got the similar identify however other parameter lists (other collection of parameters or more than a few sorts of parameters).
Assemble-Time Polymorphism
- Assemble-time polymorphism, now and again known as static polymorphism, is a kind of manner overloading. The compiler comes to a decision which solution to invoke in keeping with the process signature at construct time.
Advantages of Approach Overloading
- The use of the similar manner identify for conceptually linked duties improves the clarity and reusability of code.
- It provides a number of choices to name a technique with more than a few argument units, simplifying the calling procedure.
Examples of Approach Overloading
The next circumstances show how Java’s manner overloading mechanism purposes:
public magnificence Calculator {
// Approach so as to add two integers
public int upload(int a, int b) {
go back a + b;
}
// Overloaded manner so as to add 3 integers
public int upload(int a, int b, int c) {
go back a + b + c;
}
// Overloaded manner so as to add two double values
public double upload(double a, double b) {
go back a + b;
}
public static void major(String[] args) {
Calculator calc = new Calculator();
Device.out.println("Sum of 2 integers: " + calc.upload(5, 10)); // Calls upload(int, int)
Device.out.println("Sum of 3 integers: " + calc.upload(5, 10, 15)); // Calls upload(int, int, int)
Device.out.println("Sum of 2 doubles: " + calc.upload(5.5, 10.5)); // Calls upload(double, double)
}
}The ‘Calculator’ magnificence on this instance has 3 ‘upload’ strategies, every with a novel record of parameters:
- This provides two integers: “upload(int a, int b)”.
- So as to add 3 numbers, sort ‘upload(int a, int b, int c)’.
- So as to add two double numbers, sort “upload(double a, double b)”.
Relying at the inputs handed in, the compiler chooses which serve as to run when the ‘upload’ manner is invoked.
Regulations for Approach Overloading
1. Other Selection of Parameters
When a technique has extra parameters than essential, it could turn out to be overloaded.
public void print(String message) { }
public void print(String message, int instances) { }
2. Other Sorts of Parameters
Having too many alternative forms of parameters can crush a technique.
public void show(int quantity) { }
public void show(String textual content) { }
3. Other Order of Parameters
Converting the parameters’ order can probably overload a technique.
public void procedure(int a, double b) { }
public void procedure(double a, int b) { }
Java Scope
The accessibility and life of variables and different parts inside of a program are known as this system’s scope in Java. Comprehending the scope is an important for successfully regulating the visibility and lifecycle of variables, combating errors and making sure optimum reminiscence usage. Java defines more than a few scope sorts, together with:
Sorts of Scopes in Java
1. Magnificence Scope (Static Variables)
Magnificence-level variables, regularly known as static variables, are variables declared within a category however out of doors of any constructor, serve as, or block. All the magnificence’s static strategies can get admission to those variables, they usually stay their price in between manner calls.
public magnificence MyClass {
static int staticVariable = 10; // Magnificence scope
}2. Example Scope (Example Variables)
Magnificence-level variables, regularly known as static variables, are variables declared within a category however out of doors of any constructor, serve as, or block. All the magnificence’s static strategies can get admission to those variables, they usually stay their price in between manner calls.
public magnificence MyClass {
int instanceVariable = 20; // Example scope
}3. Approach Scope (Native Variables)
Declared variables are particular to a technique and aren’t world to it. When the process is invoked, they’re generated; when it ends, they’re destroyed. Exterior to the process, native variables aren’t to be had.
public void myMethod() {
int localVariable = 30; // Approach scope
}4. Block Scope
Variables like loops and conditionals which might be declared within a code block are simplest obtainable from inside of that block. Those variables are misplaced as quickly because the block is exited.
public void myMethod() {
if (true) {
int blockVariable = 40; // Block scope
}
// blockVariable isn't obtainable right here
}Examples of Variable Scope
public magnificence ScopeExample {
// Magnificence scope variable
static int classVar = 100;
// Example scope variable
int instanceVar = 200;
public void manner() {
// Approach scope variable
int methodVar = 300;
// Block scope variable
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int blockVar = 400;
Device.out.println("Block variable: " + blockVar);
}
// blockVar isn't obtainable right here
}
public static void major(String[] args) {
ScopeExample instance = new ScopeExample();
instance.manner();
Device.out.println("Magnificence variable: " + classVar);
Device.out.println("Example variable: " + instance.instanceVar);
// methodVar isn't obtainable right here
}
}On this instance:
- ‘classVar’ is reachable via all magnificence strategies and has magnificence scope.
- ‘instanceVar’ is particular to every example of ‘ScopeExample’ and has example scope.
- ‘methodVar’ can simplest be accessed inside of’manner()’ and has manner scope.
- “blockVar” is proscribed to the for-loop block and has a block scope.
By means of proscribing variables’ lifespans, realizing and using Java’s variable scope successfully is helping handle reminiscence and promises that variables are to be had when wanted.
Java Recursion
In Java programming, recursion is the method through which a technique calls itself to handle a subject. This system is steadily implemented to decompose advanced issues into easier-to-manage, extra minor issues. Recursion is an invaluable instrument, but it surely should be used in moderation to stop issues like countless loops and prime reminiscence usage.
How Recursion Works
Recursion is composed of 2 key elements:
1. Base Case
That is the circumstance through which the recursion concludes. A stack overflow fault would consequence from the process calling itself without end with no base case.
2. Recursive Case
At this level, to transport nearer to the bottom case, the process calls itself with altered parameters.
Instance of Recursion: Factorial Calculation
The factorial of a non-negative integer n is the fabricated from all certain integers lower than or equivalent to n. The factorial serve as may also be explained recursively as:
- n!=n×(n−1)!
- Base case: 0!=1
That is an instance of a Java recursive implementation of the factorial serve as:
public magnificence RecursionExample {
// Recursive solution to calculate factorial
public static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
go back 1; // Base case
} else {
go back n * factorial(n - 1); // Recursive case
}
}
public static void major(String[] args) {
int quantity = 5;
int consequence = factorial(quantity);
Device.out.println("Factorial of " + quantity + " is " + consequence);
}
}On this instance:
The ‘factorial’ manner calls itself with the parameter ‘n – 1’ till it reaches the bottom case the place n=0.
Advantages of Recursion
1. Simplifies Code
Recursion can simplify code via making it shorter and extra comprehensible, particularly for problems like tree traversals and a few mathematical processes that naturally have a recursive construction.
2. Sublime Answers
Recursion is a sublime solution to resolve a number of issues, together with the Tower of Hanoi, the Fibonacci series, and the quicksort manner.
Drawbacks of Recursion Efficiency
1. Efficiency
Recursive strategies might carry out extra slowly than their iterative equivalents on account of the overhead of repeated manner calls and the opportunity of stack overflow in deep recursions.
2. Reminiscence Utilization
If the recursion intensity is simply too nice, it is going to lead to stack overflow and over the top reminiscence utilization since every recursive name provides a brand new layer to the decision stack.
Conclusion
On this educational, you have been offered to the entirety about strategies in Java. It’s time to put into effect your studying and perform a little practicals. You’ll be able to additionally confer with our strategies and encapsulation educational to delve deeper into this idea. This educational will permit you to learn to practice the OOPs ideas of get admission to modifiers and encapsulation to Java categories. It’ll help you get a powerful clutch on Java programming. However if you wish to excel in total Java building, Simplilearn’s Put up Graduate Program in Complete Stack Internet Building is the easiest way to take action. The 60 hours of implemented studying and 35 coding-related workouts make the path adept at serving to you turn out to be a professional developer. You’re going to paintings on the most well liked Java frameworks, together with Hibernate and Spring throughout this path. Have any questions for us? Depart them within the feedback phase, and our professionals gets again to you sovon. Glad studying!
FAQs
1. What Is the Distinction Between a Approach Declaration and a Approach Name?
|
Side |
Approach Declaration |
Approach Name |
|
Definition |
A technique declaration defines a brand new manner, specifying its identify, go back sort, parameters, and frame. |
A technique name invokes a technique that has already been declared, executing its frame with the desired arguments. |
|
Objective |
To specify what the process will do when it is known as, together with its parameters and go back sort. |
To execute the process’s code and carry out the explained job. |
|
Elements |
– Approach identify <br> – Go back sort <br> – Parameter record <br> – Approach frame |
– Approach identify <br> – Arguments (if any) |
|
Syntax Instance |
java<br> public int upload(int a, int b) { <br> go back a + b; <br> }<br> |
java<br> int consequence = upload(5, 3);<br> |
|
Location |
Usually within a category definition, may also be declared as public, non-public, secure, or default. |
Will also be within any other manner, constructor, or initialization block. |
|
Go back Sort |
Specify a go back sort (e.g., int, void, String). |
Does now not specify a go back sort; the process being referred to as determines the go back sort. |
|
Parameters |
Pronounces the sort and collection of parameters the process will settle for. |
Passes precise values (arguments) to the process’s parameters. |
|
Execution |
Defines what occurs when the process is known as however does now not execute independently. |
Executes the code inside the manner declaration. |
|
Instance |
java<br> public void greet(String identify) { <br> Device.out.println(“Hi, ” + identify); <br> }<br> |
java<br> greet(“Alice”);<br> |
|
Overloading |
Strategies may also be overloaded via mentioning a couple of strategies with the similar identify however other parameter lists. |
Approach calls specify which overloaded solution to invoke in keeping with the arguments equipped. |
|
Scope |
Determines the scope of the process inside the magnificence (e.g., example manner, static manner). |
Is dependent upon the place the process name is made (e.g., inside of an example manner, inside of a static context). |
2. What Is Approach Overriding?
With Java, a subclass may give a selected implementation of a technique already explained in its superclass via the use of a characteristic referred to as manner overriding. The identify, parameters, and go back form of the overridden manner within the subclass should fit the ones of the process within the superclass. This concept is very important to polymorphism as it permits a subclass to change or extend the capability of a superclass manner. Runtime polymorphism is accomplished via manner overriding, through which the process that is known as at runtime is selected relying on the real form of the thing, now not its reference sort. Subclasses can specify their behaviors whilst nonetheless using the superclass’s acquainted interface.
Subclasses like “Circle” and “Rectangle” can override a superclass’s “draw()” manner, as an example, to offer distinctive implementations for drawing circles and rectangles, respectively. The power to override strategies improves the code’s flexibility and maintainability, which facilitates dealing with changes and gadget growth.
3. What Is the Objective of the ‘Go back’ Remark in a Approach?
In a technique, the ‘go back’ remark ends the methodology and might optionally go back a price to the caller. It places an finish to the process’s execution and returns the computation’s consequence to the place the process was once referred to as. This is very important for procedures that perform computations or movements that require a consequence. The ‘go back’ remark in void strategies can be utilized to finish the process early, most often for error dealing with or particular scenarios, with out returning any price.
4. What Is the ‘This’ Key phrase in Java Strategies?
The “this” key phrase in Java refers back to the present object inside of a constructor or example manner. When two variables have the similar identify, they distinguish between example and native variables. In constructors and setters, the ‘this’ key phrase is really helpful because it clarifies which variable is being mentioned. ‘this’ may also be used to name further constructors within the similar magnificence, making sure cleaner initialization and code reuse. Builders can give a boost to code clarity and save you any conflicts between magnificence attributes and parameters or native variables via the use of ‘this’ to confer with the category example explicitly.
supply: www.simplilearn.com












