Set in Java is an interface declared in java.util package deal. It extends the gathering interface that permits developing an unordered assortment or record, the place reproduction values don’t seem to be allowed. Because the identify implies, a suite in Java is used to create a mathematical set. For the reason that set extends the gathering interface, it does no longer permit reproduction components. Within the hierarchy, NavigableSet and SortedSet are the 2 interfaces that stretch set in Java.
You can not immediately use the set to create its object as it’s an interface. Therefore, it’s important to use the 4 categories, specifically EnumSet, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet, that put into effect the set interface to paintings with it. Right here, you’ll take a look at an instance to create a suite in Java the use of the HashSet elegance.
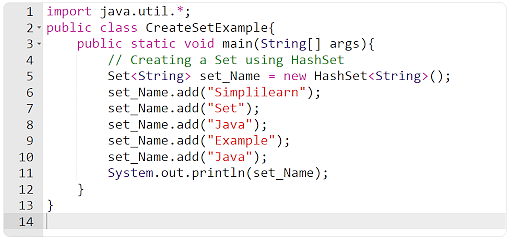

As you’ll be able to see within the above instance, the set is not going to settle for reproduction values. Therefore, it provides and prints Java handiest as soon as in set_Name.
What Are the Operations You Can Carry out on Set in Java?
A suite in Java represents a mathematical set, in which you’ll be able to carry out more than a few operations comparable to union, intersection, and distinction. You’ll do that with the assistance of addAll(), retainAll(), and removeAll() strategies for the above 3 operations, respectively. You are going to be informed concerning the strategies of the set in-detail later on this put up. However for now, take a look at what those operations do and learn how to carry out them at the set. To know this higher, imagine two units, the place set1 = [3, 5, 9, 17, 23, 41] and set2 = [2, 5, 13, 17, 41, 51]. With those units, you’ll be able to carry out the next operations.
- Union: This operation will go back the union of each set1 and set2 after getting rid of reproduction values. Therefore, the results of the union of set1 and set2 will likely be [2, 3, 5, 9, 13, 17, 23, 41, 51].
- Intersection: The intersection will handiest go back the values which might be commonplace in each units. The results of intersecting set1 and set2 will likely be [5, 17, 41].
- Distinction: This operation will delete the primary operand set values which might be commonplace with the second one operation set. For example, for those who in finding the adaptation of set1 from set2, it’ll be [3, 9, 23]. Then again, for those who in finding the adaptation of set2 from set1, it’ll be [2, 13, 51].
Apply the instance underneath with the similar units and notice if the output fits the consequences or no longer.
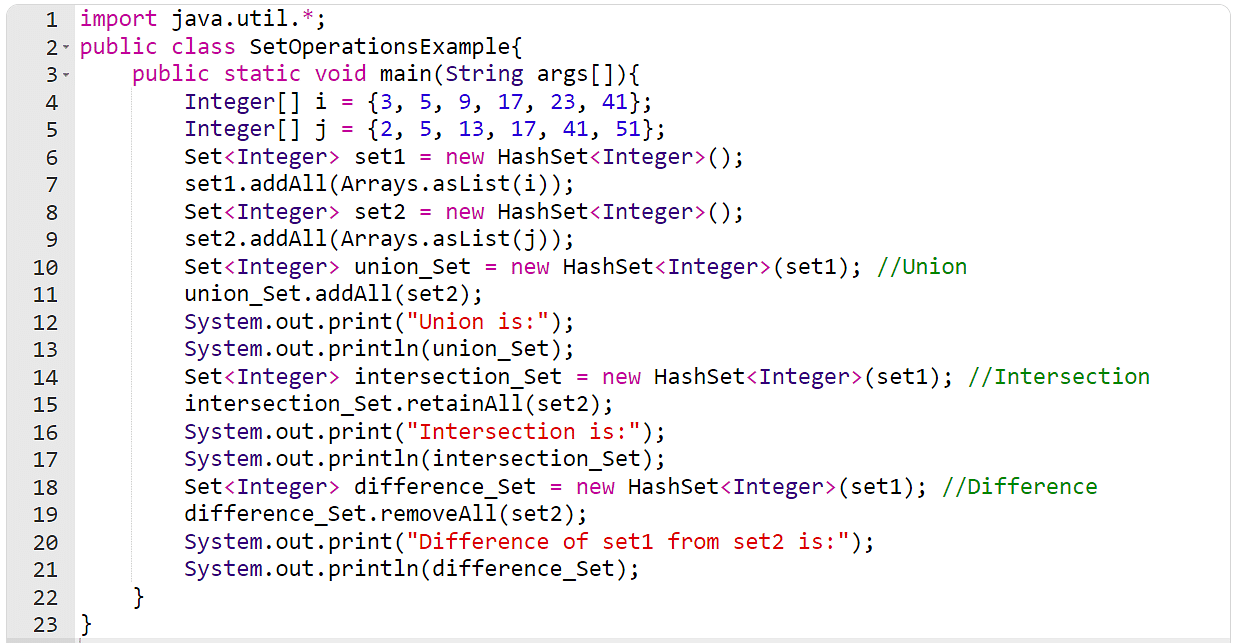
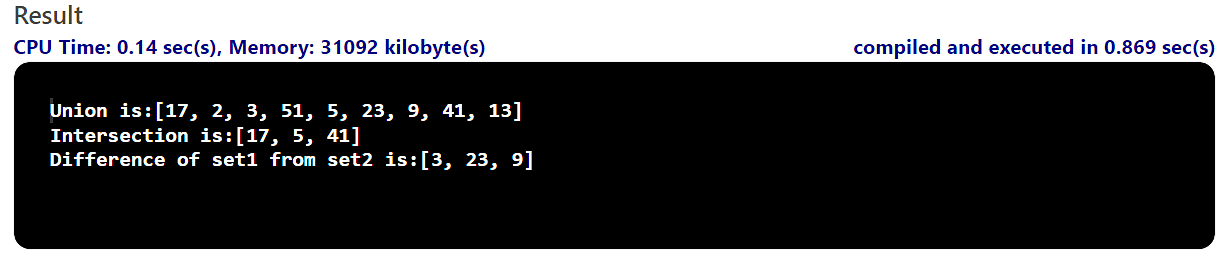
As you’ll be able to see, it has created two integer arrays and two units within the instance above. You’ve gotten then added the array values to the units. After including the values in each units respectively, you carried out all 3 operations via making a outcome set for each and every operation. The solutions you were given from the code are exactly very similar to those you calculated mathematically.
Be told extra about Java intimately and develop into job-ready on your device construction profession with our Caltech Coding Bootcamp.
What Are the Other Set Strategies To be had?
Set in Java supplies an unlimited array of strategies. You’ll use those learn how to carry out more than a few operations at the set. The desk underneath lists all of the set interface strategies at the side of the outline of what operations they carry out.
Approach |
Description |
|
upload(component) |
Provides a brand new worth to the set |
|
addAll(assortment) |
Provides all of the components of a set to the required set |
|
transparent() |
Clears all of the values of a suite (does no longer transparent the set itself) |
|
incorporates(component) |
Exams if the required component is found in a suite |
|
containsAll(assortment) |
Exams if all of the values of a set are found in a suite |
|
hashCode() |
Returns an integer hash code for the example of a suite |
|
isEmpty() |
Exams if the set is empty |
|
iterator() |
Returns an iterator object to parse in the course of the set |
|
take away(component) |
Gets rid of a specified worth from the set |
|
removeAll(assortment) |
Gets rid of the weather of a set from the set to search out the adaptation |
|
retainAll(assortment) |
Keeps the values of a set in a suite |
|
dimension() |
Returns the dimensions of the set |
|
toArray() |
Creates an array with the weather of a suite |
Examples to Use Strategies of Set in Java
Because you now know all of the set interface strategies, let’s use them one-by-one to accomplish other operations at the set. Right here, you will have to use HashSet and LinkedHashSet categories to create the set items. Alternatively, you’ll be able to additionally check out with the opposite two categories: EnumSet and TreeSet.
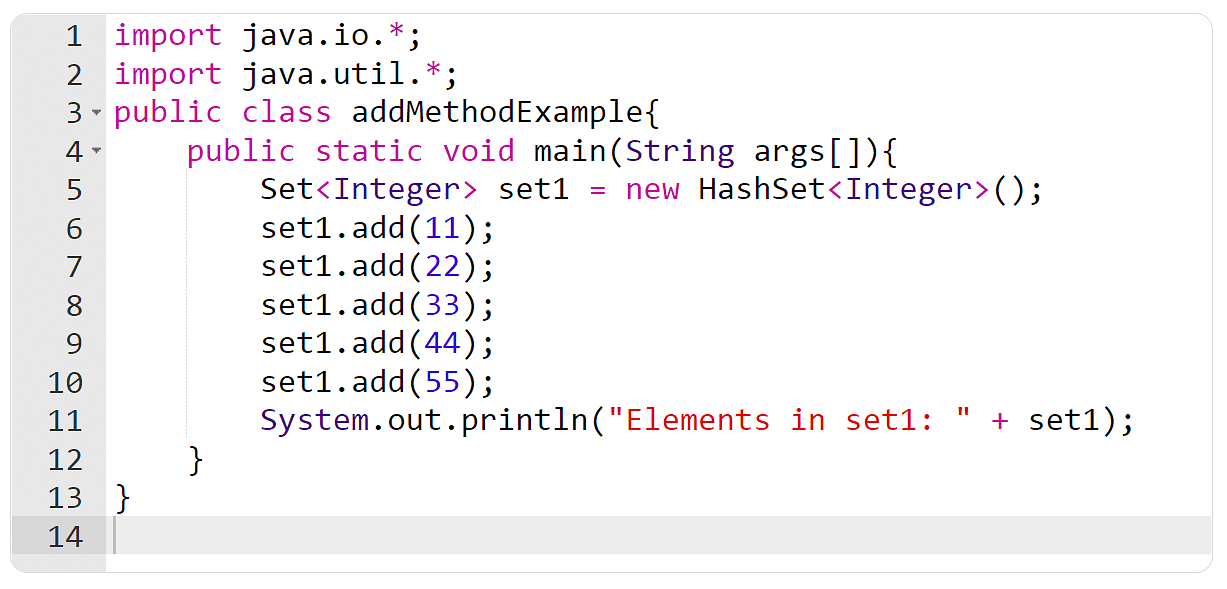
Instance 1: The upload() Approach
On this instance, you will have to create a Set object and use the upload() manner so as to add components.

Instance 2: The addAll() Approach
On this instance, you will have to create a suite and an array. You must then use the addAll() manner so as to add the array components, i.e., a set, to the set.
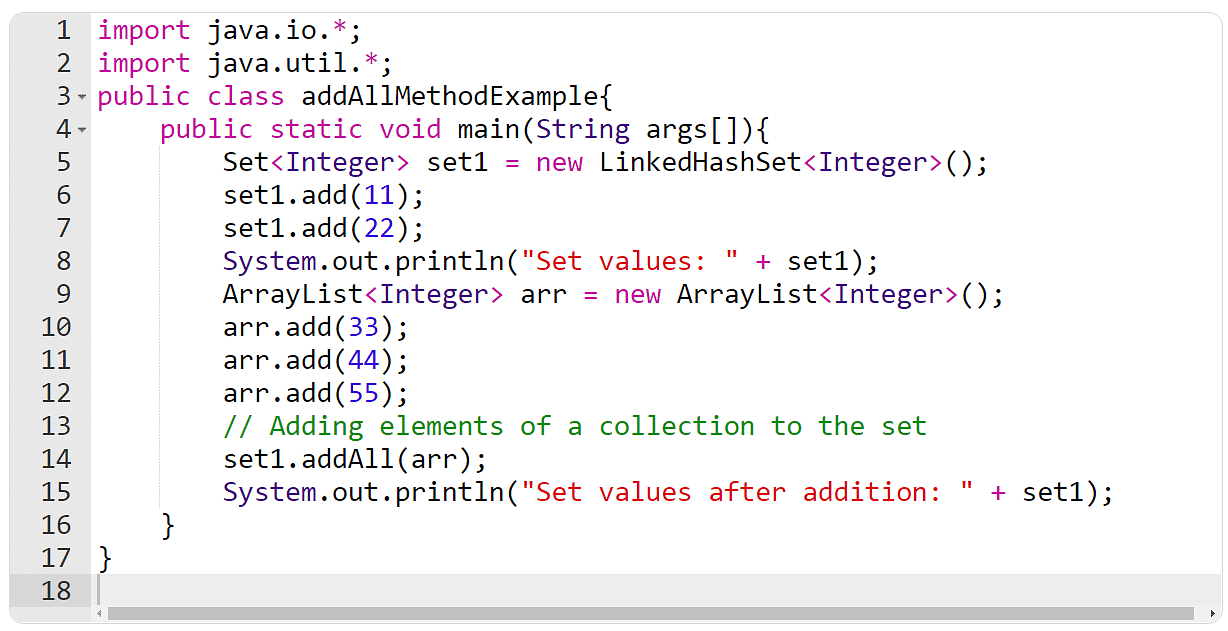
Instance 3: The transparent() Approach
You will have to create a suite object, upload a couple of components to it, after which cleared it with the transparent() manner within the following instance.
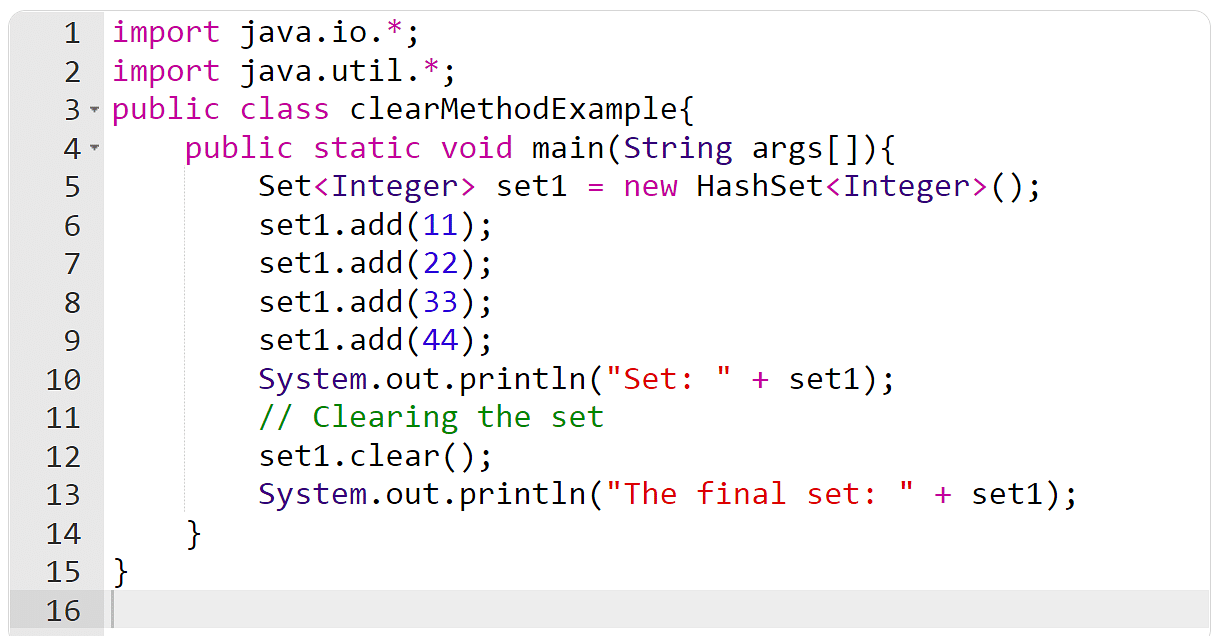

Instance 4: The incorporates() Approach
After developing a suite in Java and including components to it, you will have to use the incorporates() technique to take a look at if the required component is provide within the set or no longer.
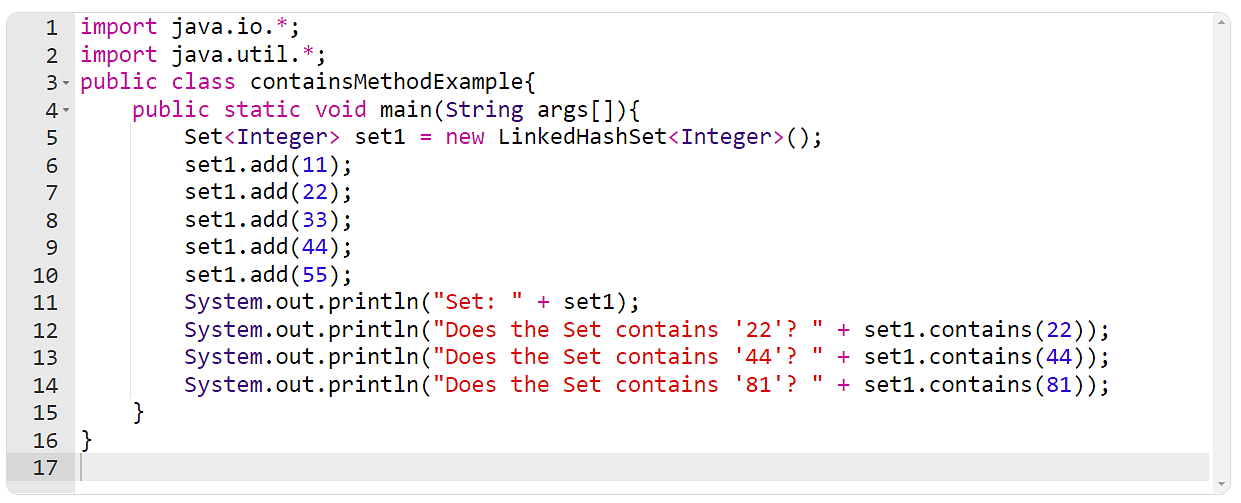

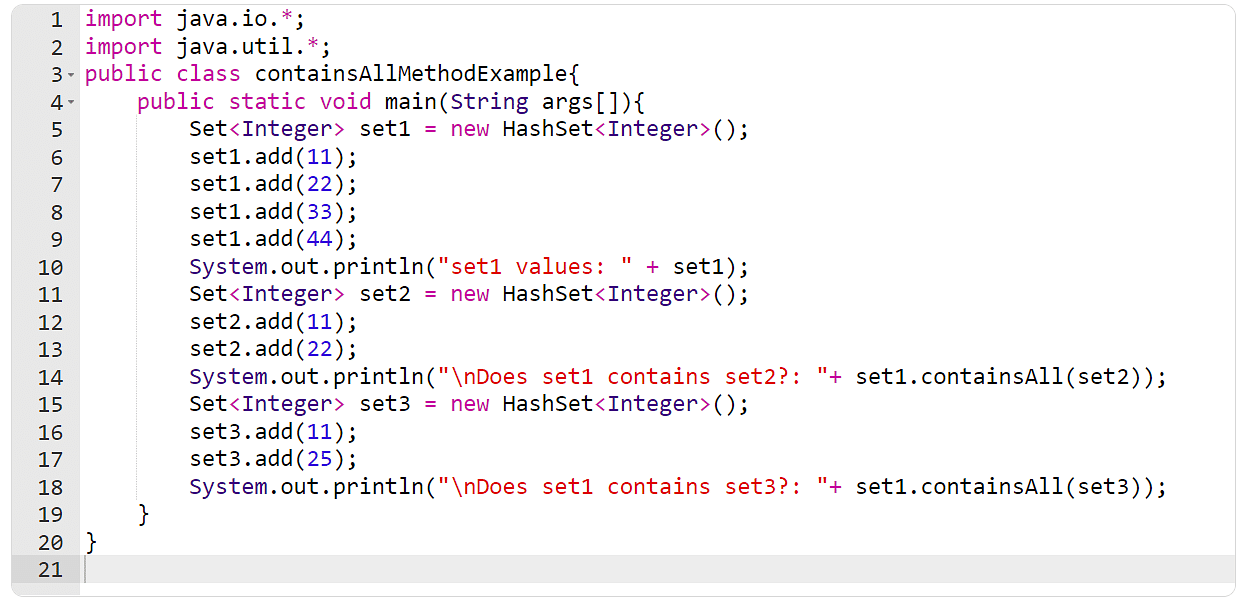
Instance 5: The containsAll() Approach
On this instance, you will have to create 3 units. Then you can use the containsAll() technique to take a look at if all of the components from the second one and 3rd set are provide within the first one.

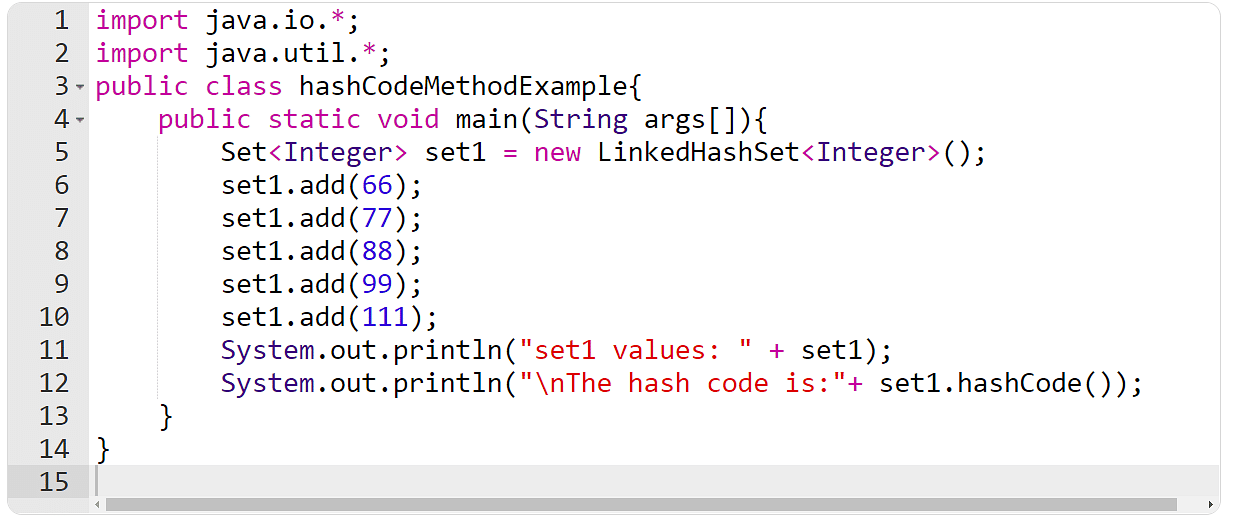
Instance 6: The hashCode() Approach
Right here, create a suite and in finding the hash code of the present example the use of the hashCode() manner within the following instance.

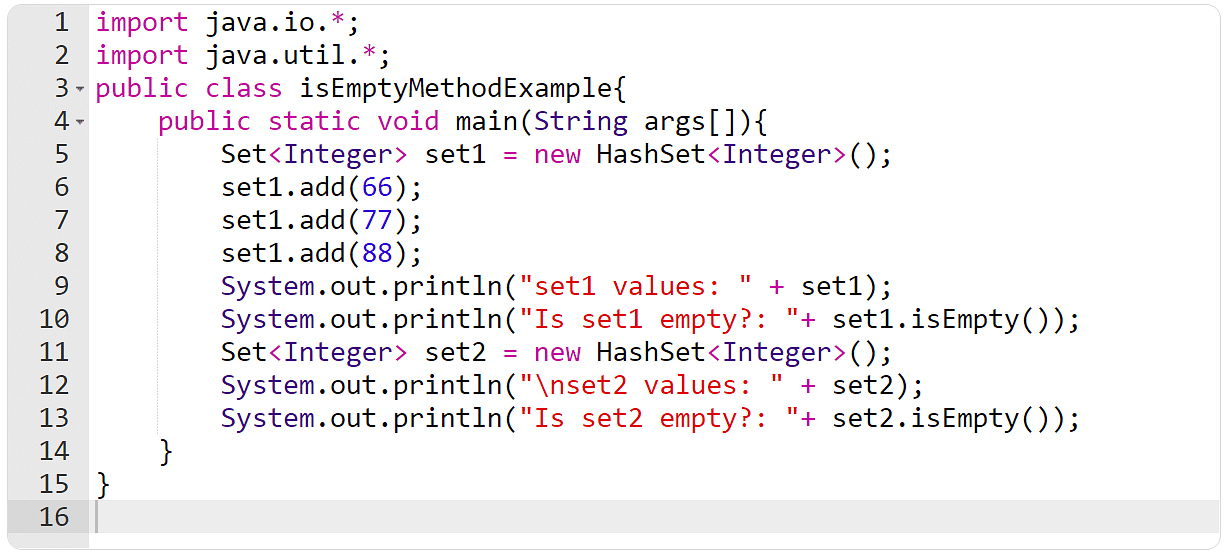
Instance 7: The isEmpty() Approach
Within the instance underneath, you will have to create two units and use the isEmpty() technique to in finding which one is empty.

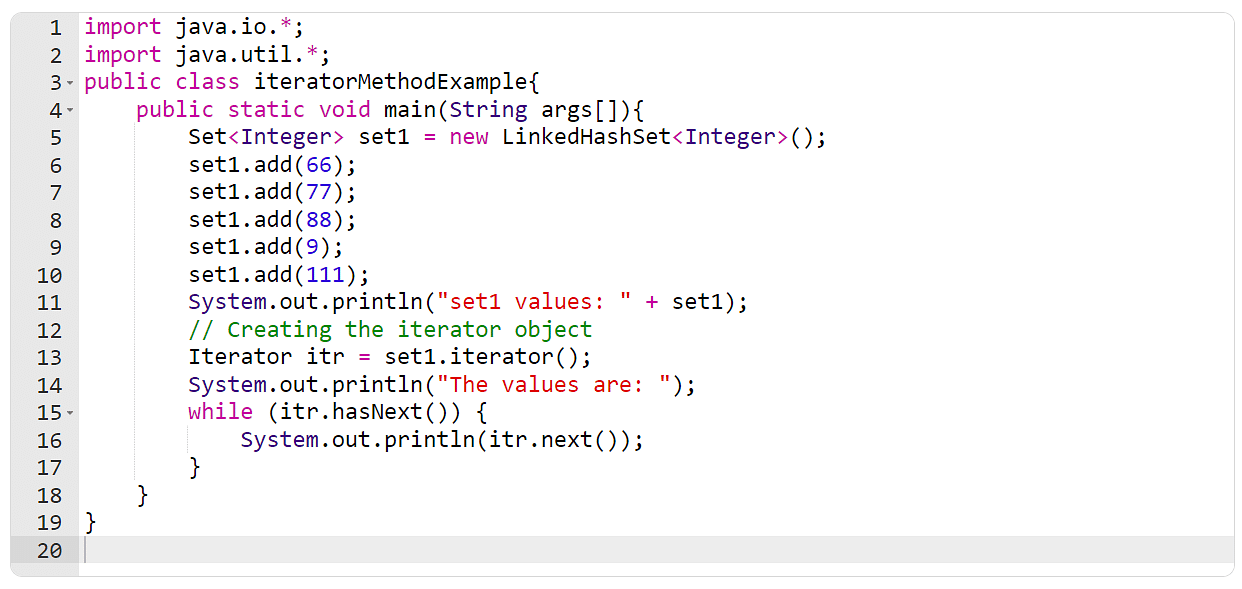
Instance 8: The iterator() Approach
For this situation, you must create a suite in Java, and use the iterator() technique to traverse thru it, and print all of the set components one-by-one.

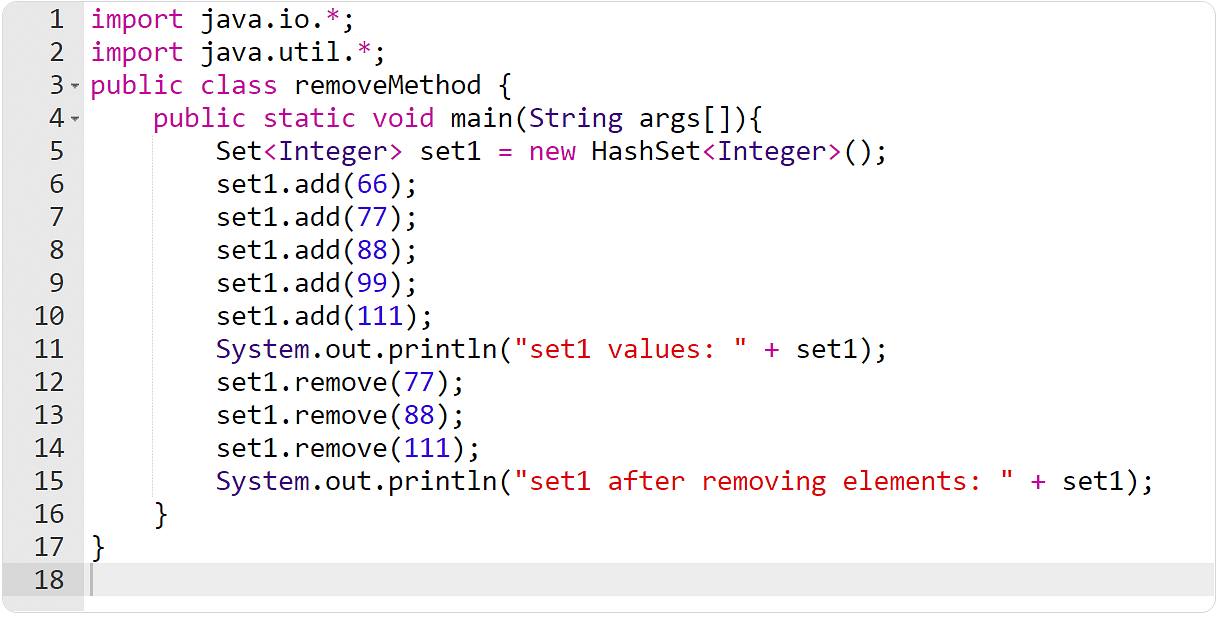
Instance 9: The take away() Approach
Right here, you will have to create a suite after which take away some components the use of the take away() manner within the underneath instance.

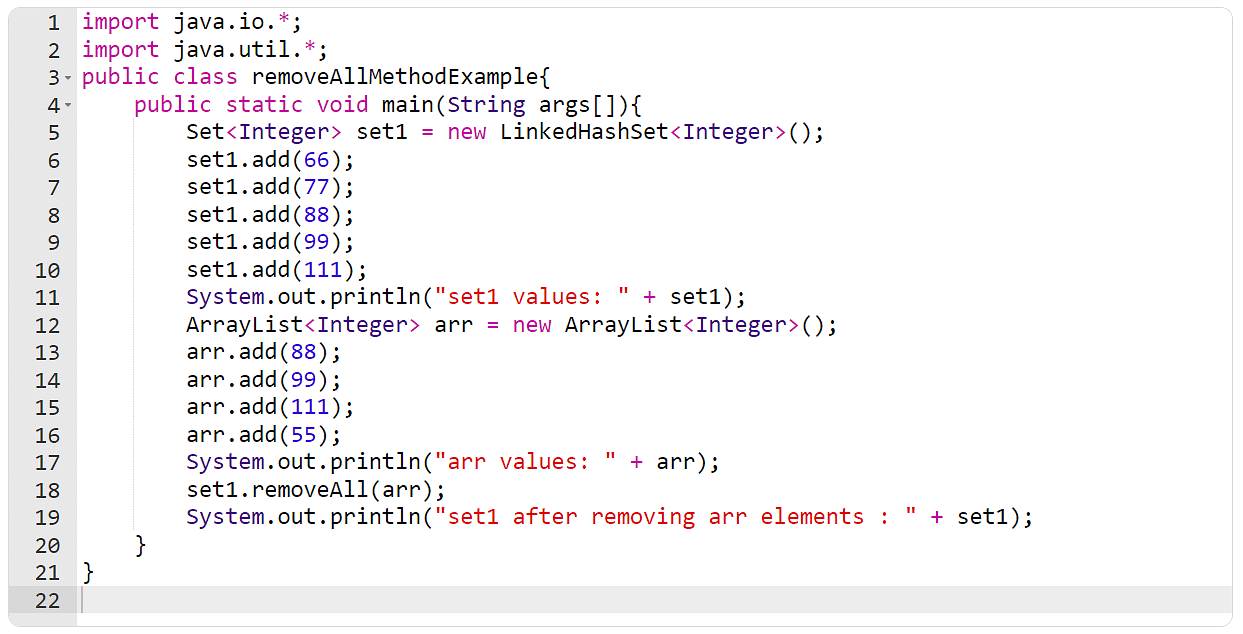
Instance 10: The removeAll() Approach
On this instance, you will have to create an array and a suite. You are going to then use the removeAll() manner to take away all of the array components provide within the set.

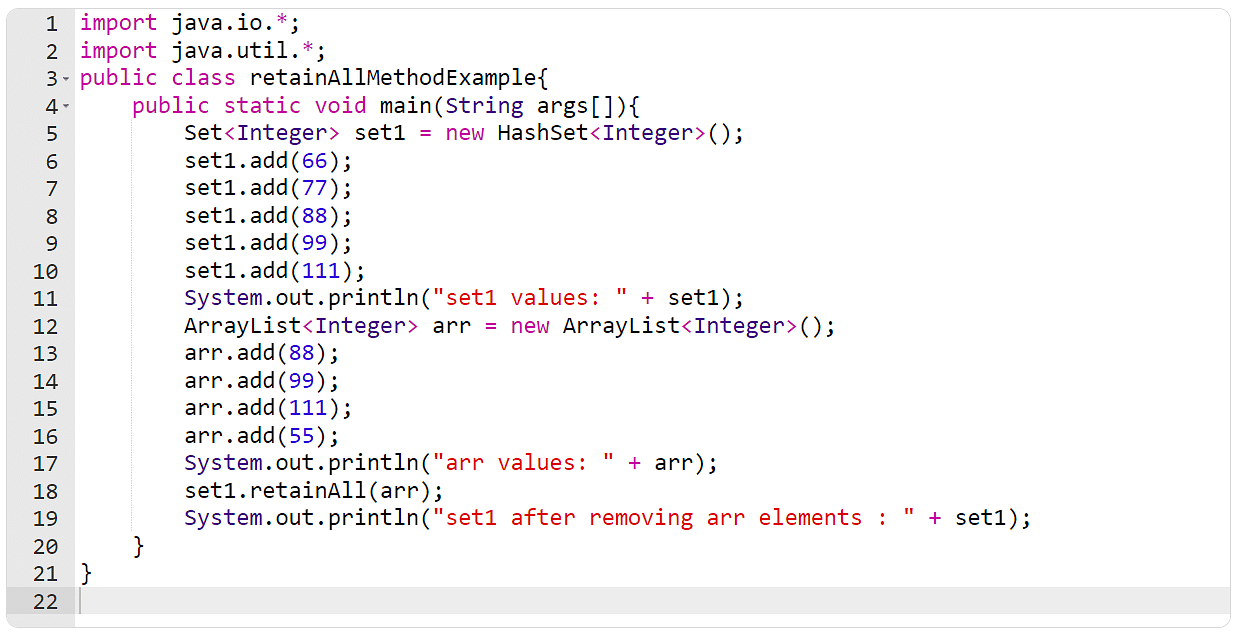
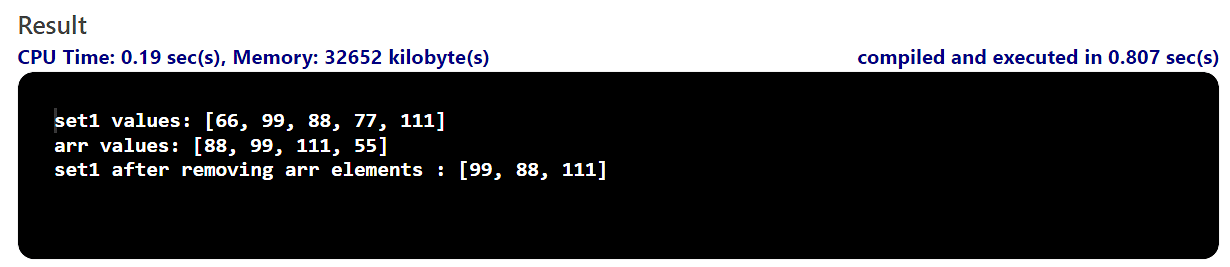
Instance 11: The retainAll() Approach
Within the instance underneath, create an array and a suite. You are going to then have to make use of the retainAll() technique to retain the array components within the set.
Instance 12: The dimensions() Approach
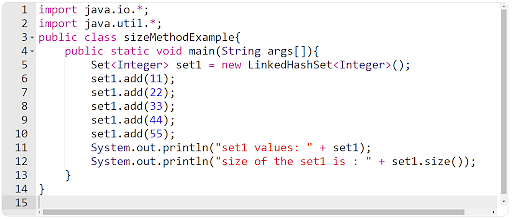
You will have to create a suite in Java after which use the dimensions() technique to in finding the set’s general dimension within the following instance.

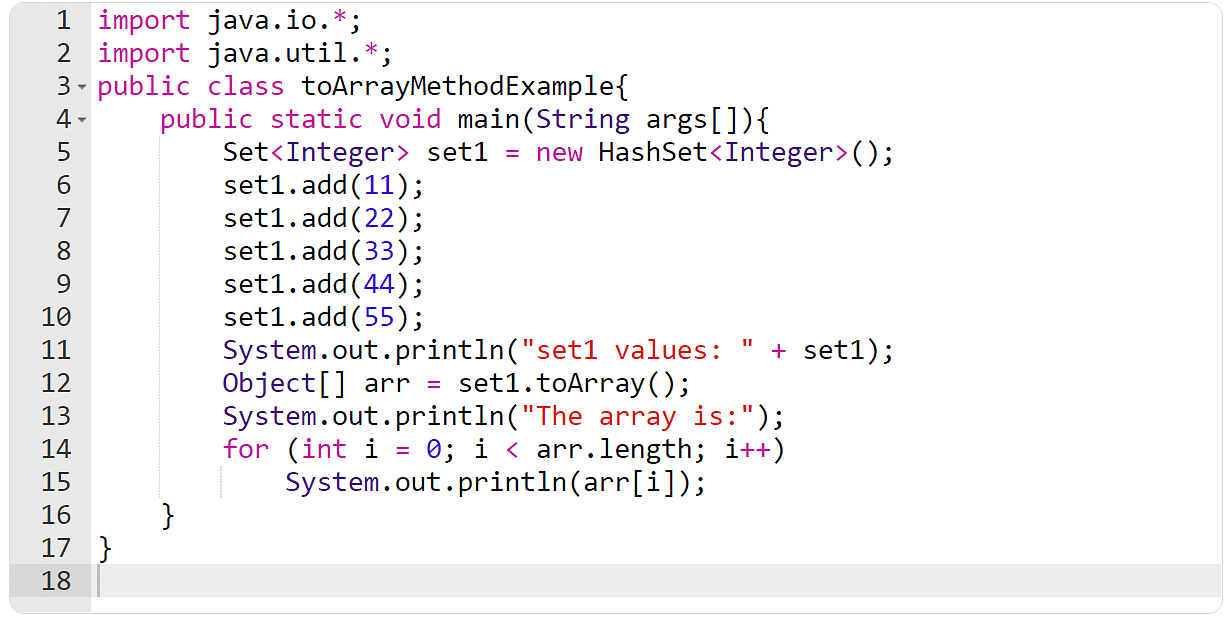
Instance 13: The toArray() Approach
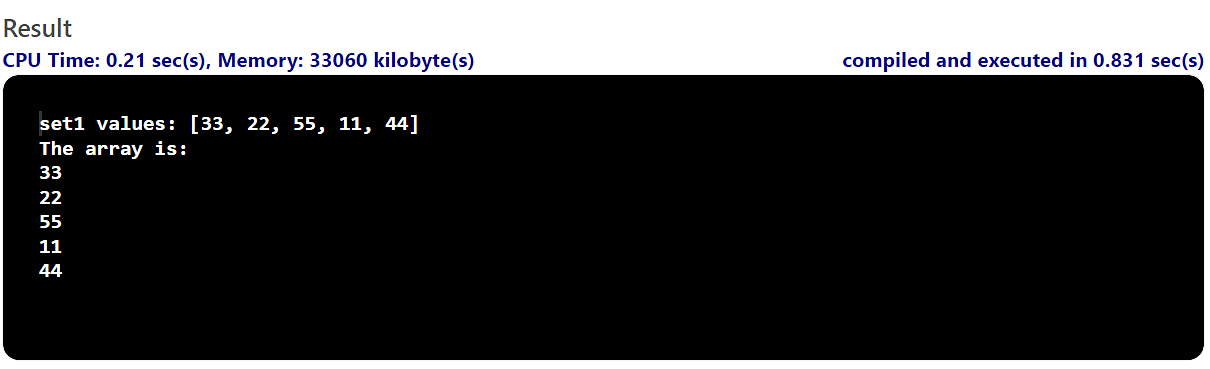
Within the following instance, you will have to create a suite and use the toArray() technique to create an array of the similar components.
Conclusion
With this, you’ve got reached the tip of this text titled ‘Set in Java’. If you want to additional your wisdom in Java and take it up as a profession, certification is very beneficial. Be told extra about units in Java and different complex ideas via making use of to Simplilearn’s On-line Java Certification Path and excel in Java device construction.
Do you’ve got any questions for us? Go away them within the feedback segment of this text. Our mavens gets again to you at the similar, quickly.
Glad studying!
supply: www.simplilearn.com












