C++ is without doubt one of the most well liked programming languages international. It’s a longer model of the C programming language and in part follows the Object-Orientated Programming (OOPs) thought. Like different OOPs languages, even C++ permits basics corresponding to encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and so forth. On this article, you’ll center of attention on digital purposes in C++ which might be used to reach polymorphism.
What’s a Digital Serve as in C++?
A digital serve as in C++ is a base elegance member serve as that you’ll be able to redefine in a derived elegance to reach polymorphism. You’ll be able to claim the serve as within the base elegance the use of the digital key phrase. Whenever you claim the serve as within the base elegance, you’ll be able to use a pointer or reference to name the digital elegance and execute its digital model within the derived elegance. Thus, it asks the compiler to decide the item’s sort all the way through run-time and create a serve as bind (past due binding or dynamic linkage).
A digital serve as in C++ is helping be sure to name the proper serve as by means of a reference or pointer. The C++ programming language permits you simplest to make use of a unmarried pointer to check with all of the derived elegance items. Because the pointer refers to all of the derived items, calling it is going to persistently execute the serve as within the base elegance. You’ll be able to conquer this problem with a digital serve as in C++ because it is helping execute the digital model of the derived elegance, which is finished on the run-time.
What Are the Laws of Digital Serve as in C++?
There are a couple of laws you wish to have to practice to create a digital serve as in C++. Those laws are:
- The purposes can’t be static
- You derive them the use of the “digital” key phrase
- Digital purposes in C++ must be a member of a few different elegance (base elegance)
- They may be able to be a pal serve as of some other elegance
- The prototype of those purposes will have to be the similar for each the bottom and derived elegance
- Digital purposes are out there the use of object tips
- Redefining the digital serve as within the derived elegance is non-compulsory, nevertheless it must be outlined within the base elegance
- The serve as name resolving is finished at run-time
- You’ll be able to create a digital destructor however now not a constructor
Our Unfastened Lessons with Cetificate
The use of a Digital Serve as in C++
Now that you recognize the basics of the digital serve as in C++, it’s time to go directly to an instance of the use of it. Within the underneath instance, you’ll create a base elegance and a derived elegance. In each categories, you’ll create two purposes: Output and Show. To peer the adaptation between the digital serve as and a normal serve as, you’ll simplest claim the Output serve as of the bottom elegance as digital, and stay the show serve as as it’s.
#come with <iostream>
the use of namespace std;
elegance Base{
public:
digital void Output(){
cout << “Output Base elegance” << endl;
}
void Show(){
cout << “Show Base elegance” << endl;
}
};
elegance Derived : public Base{
public:
void Output(){
cout << “Output Derived elegance” << endl;
}
void Show()
{
cout << “Show Derived elegance” << endl;
}
};
int primary(){
Base* bpointr;
Derived dpointr;
bpointr = &dpointr;
// digital serve as binding
bpointr->Output();
// Non-virtual serve as binding
bpointr->Show();
}
Output:
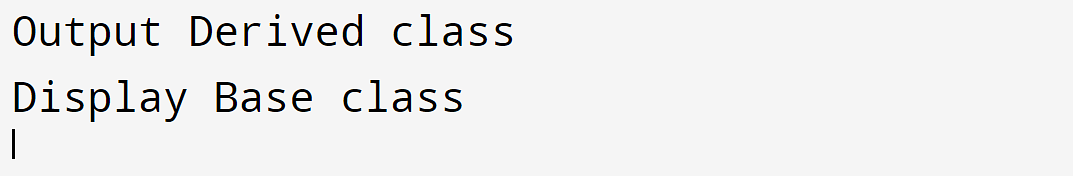
As you’ll be able to see within the output, the output serve as gave the outcome “Output Derived elegance, ” and the Derived serve as gave the outcome “Show Base elegance”. That’s since the pointer of the bottom elegance referred to the digital output serve as of the derived elegance, and the non-virtual show serve as of the bottom elegance.
Collect-Time VS Runtime Conduct of Digital Purposes in C++
A digital serve as in C++ shows two various kinds of habits: compile-time and runtime.
|
Collect-time habits |
Runtime habits |
|
|
Choice title |
Early binding |
Overdue binding |
|
How is it completed |
The kind of pointer |
Relying at the location the place the pointer is pointing |
Imagine the instance underneath to know the habits of digital purposes higher.
#come with <iostream>
the use of namespace std;
elegance base {
public:
digital void display(){
cout << “display base elegance” << endl;
}
void print(){
cout << “print base elegance” << endl;
}
};
elegance derived : public base {
public:
void display(){
cout << “display derived elegance” << endl;
}
void print(){
cout << “print derived elegance” << endl;
}
};
int primary(){
base* bpointr;
derived dev;
bpointr = &dev;
// runtime binding
bpointr->display();
// assemble time binding
bpointr->print();
}
Output:

Since you’ve declared the display serve as as digital within the above code, it is going to be sure at runtime. Therefore, the output displays the derived elegance because the pointer that was once pointing to that location. Alternatively, the print was once a non-virtual serve as; it exhibited compile-time habits, and the output was once print base elegance.
What’s a Natural Digital Serve as in C++?
A natural digital serve as in C++, sometimes called the do-nothing serve as, is a digital serve as that doesn’t carry out any job. It is just used as a placeholder and does now not include any serve as definition (do-nothing serve as). It’s declared in an summary base elegance. These kinds of categories can not claim any items of their very own. You derive a natural digital serve as in C++ the use of the next syntax:
Digital void class_name() = 0;
Instance of Natural Digital Purposes in C++
#come with <iostream>
the use of namespace std;
elegance Base{
public:
digital void Output() = 0;
};
elegance Derived : public Base{
public:
void Output()
{
std::cout << “Elegance derived from the Base elegance.” << std::endl;
}
};
int primary(){
Base *bpointr;
Derived dpointr;
bpointr = &dpointr;
bpointr->Output();
go back 0;
}
Output:

Conclusion
On this article, you’ve explored digital purposes in C++ together with easy examples. You have got additionally observed what a natural digital serve as in C++ is. You’ll be able to now create digital purposes of your personal and use them to execute derived variations of base elegance purposes and succeed in run-time polymorphism via it.
With digital purposes, you’ll be able to additionally conquer the issue of a pointer at all times pointing in opposition to the bottom elegance. If you wish to be informed extra about such elementary ideas of C++, you’ll be able to check with our C++ Instructional for Novices. The tutorials are designed that can assist you grab quite a lot of subjects and ideas of C++ programming and will let you excel in C++ building.
Have any questions for us? Go away them within the feedback phase of this newsletter. Our mavens will will let you with the similar, ASAP!
supply: www.simplilearn.com












