A serve as is a constituent piece of code that plays a particular process in a program. Now, to know serve as overriding, you will have to perceive inheritance first, as enforcing inheritance is necessary to override a serve as. Inheritance is one among extra essential ideas of OOPs that permits a derived elegance to inherit the homes of its mother or father elegance. Serve as overriding offers you a option to override an present capability of a category within a selected derived elegance. This can also be helpful when a kid elegance calls for its personal model of a capability.
Now, perceive this with the assistance of an instance. Imagine a car production corporate “Ford”. A “Automotive” manufactured by way of this corporate inherits homes like logo title and car sort i.e. “4 Wheeler” from it. Alternatively, the “Automotive” could have a extra particular car sort like “Sports activities car”. So, the car sort serve as of the category “Ford” can also be overridden within the elegance “Automotive” having its personal definition of the serve as.
What’s Serve as Overriding in C++?
Serve as overriding in C++ is an idea wherein you’ll be able to outline a serve as of the similar title and the similar serve as signature (parameters and their knowledge varieties) in each the bottom elegance and derived elegance with a unique serve as definition. It redefines a serve as of the bottom elegance throughout the derived elegance, which overrides the bottom elegance serve as. Serve as overriding is an implementation of the run-time polymorphism. So, it overrides the serve as on the run-time of this system.
Syntax to Enforce Serve as Overriding in C++
The next is the overall syntax to put in force means overriding in C++:
public elegance Base{
access_modifier:
// overridden serve as
return_type function_name(){}
};
}
public elegance Derived : public Base {
access_modifier:
// overriding serve as
return_type function_name(){}
};
}
It redefines the serve as of the bottom elegance within the derived elegance, so the return-type, function_name, and function_parameters will have to be the similar to succeed in serve as overriding.
How Does Serve as Overriding Paintings in C++?
To know the operating of serve as overriding in C++, imagine a easy instance:
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
elegance parent_class
{
public:
digital void print()
{
cout << “nThis is print() means”
” of BaseClass”;
}
};
elegance derived_class : public parent_class
{
public:
// Serve as Overriding – new definition of
// print means of base elegance
void print()
{
cout << “nThis is print() means”
” of the Derived Magnificence”;
}
};
// Driving force code
int major()
{
derived_class obj;
obj.print();
}
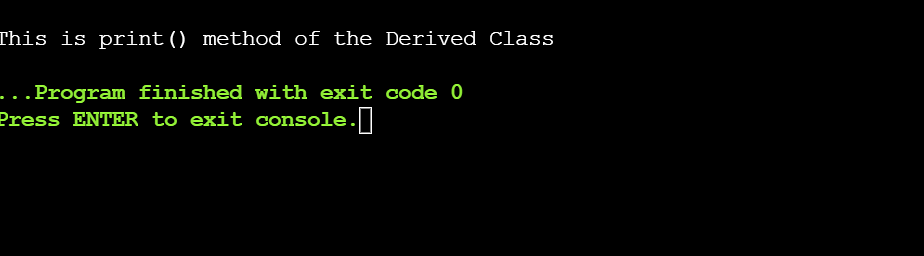
Within the above instance, it defines the print() serve as in each the bottom elegance, this is, parent_class in addition to the derived elegance i.e., derived_class with the similar serve as signature however a unique serve as definition. So, while you get admission to the print() serve as the usage of the derived elegance object d_obj, the derived elegance serve as overrides the bottom elegance serve as (imagine the beneath code snippet).
Our Loose Lessons with Certificates
Instance of Serve as Overriding From Actual-life
An instance of serve as overriding can also be observed in quite a lot of forms of cars. As an example, we’ve got a base elegance referred to as “Car” that has a serve as referred to as “power”, which merely prints out a message pronouncing “Riding the car”. Now, let’s consider we’ve got two derived categories, “Automotive” and “Motorbike”, which each inherit from the “Car” elegance. Each “Automotive” and “Motorbike” categories have their very own implementation of the “power” serve as this is extra particular to their sort. For instance, the “Automotive” elegance would possibly print out “Riding the automobile” whilst the “Motorbike” elegance would possibly print out “Driving the bike”. After we name the “power” serve as on an object of the “Automotive” elegance or the “Motorbike” elegance, the implementation within the derived elegance will probably be finished as a substitute of the implementation within the base elegance.
Instance
Components of Serve as Declaration in C++
Earlier than we dive deeper into serve as overriding, let’s take a snappy take a look at the weather of a serve as declaration in C++:
Basic Syntax:
return_type function_name (parameters) {
// Serve as frame
}
- Go back Sort: The go back form of a job defines the kind of price which that process returns. As an example, if a job returns an integer when the go back form of that process could be “int”.
- Serve as Identify: The serve as title is the identifier used to put in force the serve as from the opposite portions of the code. The serve as title will have to be significant and will show the aim of the serve as.
- Parameters: A serve as’s parameters are the inputs that can be utilized within the serve as frame to do calculations or manipulate any knowledge sort with 0 or extra parameters.
- Serve as Frame: The serve as frame is the code applied when the serve as is began. It has the good judgment for the serve as.
Calling a Serve as: A serve as is known as the usage of its title adopted by way of parentheses containing any essential arguments. For instance, to name a serve as named “myFunction” that takes two integers as arguments, the syntax could be “myFunction(5, 10)”.
Benefits of Serve as Overriding
The concept that of means overriding in C++ serves quite a lot of benefits. One of the crucial main benefits are as follows:
- Serve as overriding is helping to support the clarity of the code.
- If each the kid elegance and base elegance have the similar serve as, it’ll now not impact the independence of the kid elegance serve as.
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
//base elegance
elegance parent_class
{
public:
//serve as to calculate house of a 2D form
digital void house(int side1, int side2)
{
//serve as definition
cout << “Space is: ” << (side1 * side2) << endl;
}
};
//derived elegance
elegance derived_class : public parent_class
{
public:
// serve as to calculate house of a triangle
void house(int side1, int side2)
{
//serve as definition
cout << “Space is: ” << (0.5 * side1 * side2) << endl;
}
};
int major()
{
parent_class sq., rectangle;
derived_class triangle;
// house() of base elegance is known as
sq..house(2, 2);
rectangle.house(4, 5);
// house() of derived elegance is known as
triangle.house(4, 5);
go back 0;
}

Within the instance above, the derived elegance had its personal implementation of the world() serve as. When an object of the derived elegance calls the world() serve as, the overriding serve as is known as, which calculates the world of a triangle.
- Overriding a serve as saves the reminiscence, will increase the consistency of code, and complements code reusability.
- A serve as with the similar title can be utilized to accomplish other operations and therefore makes the code blank.
Examples of Serve as Overriding in C++
The next examples illustrate other eventualities to get admission to the overridden serve as and the overriding serve as.
Instance 1: Gaining access to Overriding Serve as
This case illustrates how you can get admission to the overriding serve as (that’s the re-defined serve as throughout the derived elegance).
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
// outline the bottom elegance
elegance parent_class
{
public:
// outline overridden serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the bottom elegance serve as.n”;
}
};
// outline the derived elegance
elegance derived_class : public parent_class
{
public:
// outline overriding serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the derived elegance serve as.n”;
}
};
int major()
{
// create object of derived elegance
derived_class obj;
// name the overriding serve as
obj.display_message();
go back 0;
}
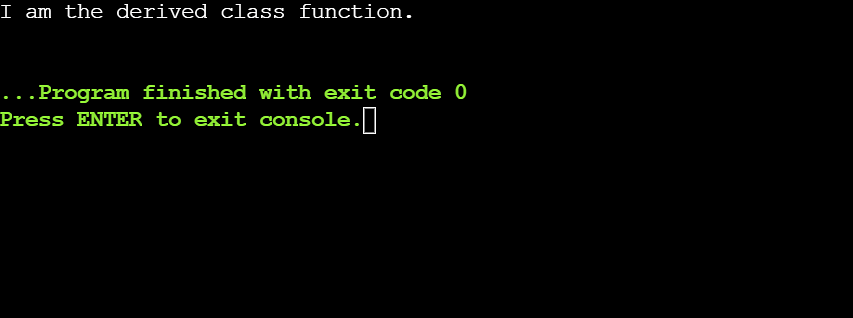
Within the above instance, it redefines the serve as display_message() of the bottom elegance within the derived elegance. The go back sort and the serve as signature are the similar in each categories. The display_message() serve as of the bottom elegance overrides the display_message() serve as of the bottom elegance. So, when the derived elegance object makes a choice to the display_message() serve as, it accesses the display_message() of the derived elegance.
Instance 2: Gaining access to Overridden Serve as
As you might have observed within the earlier instance, the item of the derived elegance accesses the overriding serve as (explained throughout the derived elegance). Alternatively, you’ll be able to additionally get admission to the overridden serve as (explained throughout the base elegance) by way of an example of the derived elegance.
The next instance illustrates how you can get admission to the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance the usage of the example of the derived elegance.
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
// outline the bottom elegance
elegance parent_class
{
public:
// outline overridden serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the bottom elegance serve as.nn”;
}
};
// outline the derived elegance
elegance derived_class : public parent_class
{
public:
// outline overriding serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the derived elegance serve as.nn”;
}
};
int major()
{
// create circumstances of the derived elegance
derived_class obj1, obj2;
// name the overriding serve as
obj1.display_message();
// name the overridden serve as of the Base elegance
obj2.parent_class::display_message();
go back 0;
}
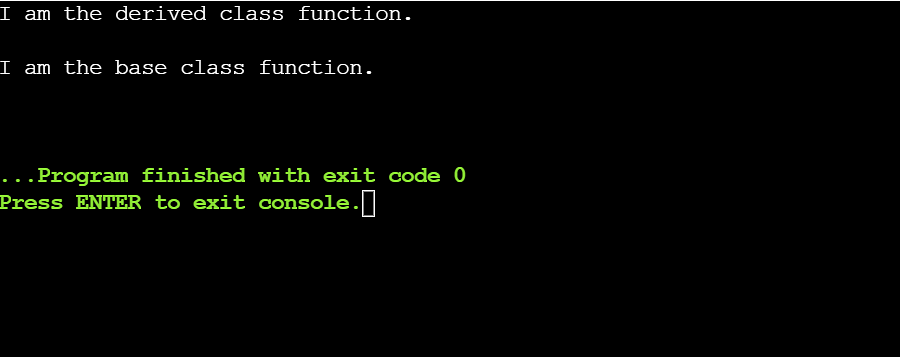
Within the above instance, the scope answer operator (::) is used to get admission to the overridden serve as, display_message() of the bottom elegance. The commentary obj2.parent_class::display_message() calls the display_message() serve as explained throughout the base elegance.
Instance 3: Gaining access to Overridden Serve as Throughout the Derived Magnificence
The overridden serve as of the bottom elegance may also be accessed by way of the derived elegance the usage of the scope answer operator (::). On this manner, you’ll be able to additionally get admission to the overridden serve as by way of the example of the derived elegance.
The next instance illustrates how you can get admission to the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance throughout the derived elegance.
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
// outline the bottom elegance
elegance parent_class
{
public:
// outline overridden serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the bottom elegance serve as.nn”;
}
};
// outline the derived elegance
elegance derived_class : public parent_class
{
public:
// outline overriding serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the derived elegance serve as.nn”;
// name the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance
parent_class::display_message();
}
};
int major()
{
// create circumstances of the derived elegance
derived_class obj1, obj2;
// each the overridden and the
// overriding serve as will probably be accessed right here
obj1.display_message();
go back 0;
}
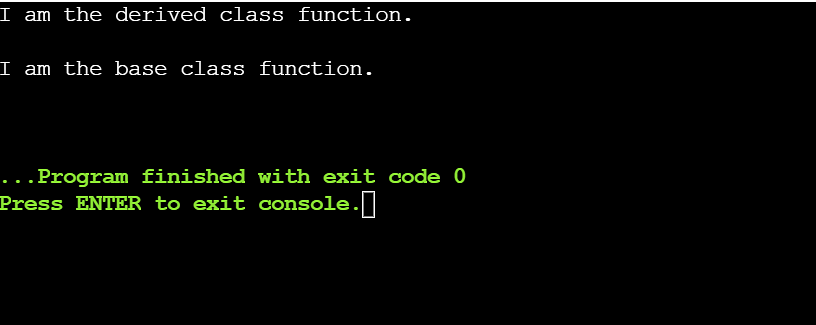
Within the above instance, the display_message() serve as of the bottom elegance is known as throughout the display_message() of the derived elegance the usage of the scope answer operator. This permits the example of the derived elegance to get admission to the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance not directly.
Instance 4: Gaining access to the Overridden Serve as The usage of a Pointer
You’ll additionally get admission to the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance the usage of a pointer of the bottom elegance sort pointing to the item of the derived elegance.
The next instance illustrates how you can get admission to the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance the usage of a pointer of the bottom elegance sort.
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
// outline the bottom elegance
elegance parent_class
{
public:
// outline overridden serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the bottom elegance serve as.nn”;
}
};
// outline the derived elegance
elegance derived_class : public parent_class
{
public:
// outline overriding serve as
void display_message()
{
cout << “I’m the derived elegance serve as.nn”;
// name the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance
}
};
int major()
{
// create circumstances of the derived elegance
derived_class obj;
// pointer of base elegance sort
parent_class *ptr = &obj;
// name the overridden serve as
ptr->display_message();
go back 0;
}
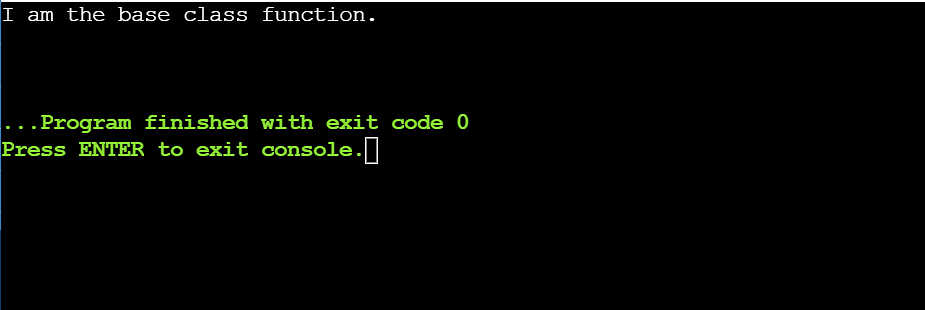
Within the above instance, it creates a pointer of the bottom elegance sort. The commentary parent_class *ptr = &obj creates a pointer ptr, which issues to the item of the derived elegance. Even supposing the pointer is pointing to the derived elegance object, when the display_message() serve as is known as, it executes the overridden serve as of the bottom elegance. It’s because the pointer is of the bottom elegance sort.
Diversifications in Serve as Overriding (With Examples)
Serve as overriding provides larger flexibility and customization in programming. Let’s speak about the diversities of means overriding in C++ with examples.
Elementary Serve as Overriding
Probably the most elementary serve as overriding comes to redefining one way with the similar title and signature in a subclass. For instance:
Instance
elegance Animal {
public:
digital void discuss() {
std::cout << “Animal speaks!” << std::endl;
}
};
elegance Canine : public Animal {
public:
void discuss() override {
std::cout << “Canine barks!” << std::endl;
}
};
int major() {
Animal* animal = new Canine();
animal->discuss(); // prints “Canine barks!”
delete animal;
go back 0;
}
On this instance, the superclass Animal has one way discuss(), and a subclass Canine that overrides this technique with its implementation. After we create an example of Canine and speak to its discuss() means via a pointer to the Animal base elegance, we get the habits we predict: for the canine to bark.
Digital Serve as Overriding
In digital serve as overriding, a serve as within the base elegance is said with the phrase “digital,” indicating {that a} subclass would possibly override it. When the serve as is known as by means of a pointer or connection with the bottom elegance, the serve as’s implementation within the required subclass is known as.
Instance:
elegance Form {
public:
digital void draw() {
cout << “Drawing Form” << endl;
}
};
elegance Circle: public Form {
public:
void draw() {
cout << “Drawing Circle” << endl;
}
};
int major() {
Form *form;
Circle circle;
form = &circle;
shape->draw();
go back 0;
}
On this instance, the Form elegance has a digital serve as referred to as draw(), which is overridden by way of the Circle elegance. When the draw() serve as is known as via a pointer to the Form elegance, the serve as’s implementation within the Circle elegance is known as, leading to “Drawing Circle” being revealed to the console.
Non-Digital Serve as Overriding
In non-virtual serve as overriding, a subclass implements a non-virtual serve as within the base elegance. This change is much less commonplace than digital serve as overriding as a result of it’s much less versatile and can’t be used for polymorphism.
Instance:
elegance Form {
public:
void draw() {
cout << “Drawing Form” << endl;
}
};
elegance Circle: public Form {
public:
void draw() {
cout << “Drawing Circle” << endl;
}
};
int major() {
Form *form;
Circle circle;
form = &circle;
shape->draw();
go back 0;
}
Serve as Overloading vs. Serve as Overriding
Even if each serve as overloading and serve as overriding supply some way to succeed in polymorphism, they vary in relation to a number of facets together with their definition, implementation, and utilization.
Serve as Overloading
Serve as overloading happens when two or extra purposes have the similar title along side the similar go back sort however with other parameters.
Instance
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
elegance function_overload
{
public:
// findArea() serve as with one integer parameter
void findArea(int side1)
{
cout << “The world is: “;
cout << (side1 * side1) << “nn”;
}
// findArea() serve as with two integer parameters
void findArea(int side1, int side2)
{
cout << “The world is: “;
cout << (side1 * side2) << “nn”;
}
};
int major()
{
function_overload obj;
// name first findArea() serve as
obj.findArea(5);
// name 2nd findArea() serve as
obj.findArea(5, 6);
go back 0;
}
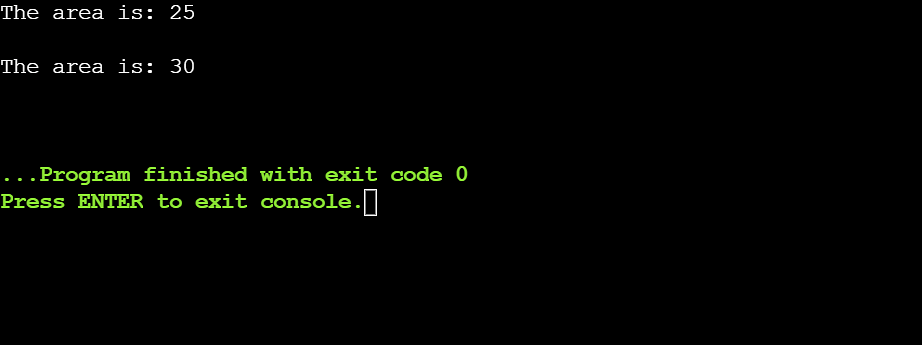
Within the above instance, the findArea() serve as is the overloaded serve as. When the serve as is known as, the compiler fits the arguments with the serve as signature and it executes the matched serve as. So, the commentary findArea(5) corresponds to the findArea() serve as with one integer parameter, and the commentary findArea(5, 6) corresponds to the findArea() serve as having two integer parameters.
Serve as Overriding
When it redefines a serve as of the bottom elegance in a derived elegance with the similar signature i.e., title, go back sort, and parameter however with a unique definition, it is known as serve as overriding.
Instance
#come with <iostream>
the usage of namespace std;
elegance function_override
{
public:
// findArea() serve as of the bottom elegance
// it’s the overridden serve as
void findArea(int aspect)
{
cout << “The world is: “;
cout << (aspect * aspect) << “nn”;
}
};
elegance derived_class : public function_override
{
public:
// findArea() serve as of the derived elegance
// it’s the overriding serve as
void findArea(int aspect)
{
cout << “The world is: “;
cout << (0.5 * aspect * aspect) << “nn”;
}
};
int major()
{
derived_class obj;
// overriding serve as is known as
obj.findArea(5); // 0.5 * 5* 5 is outlined
go back 0;
}
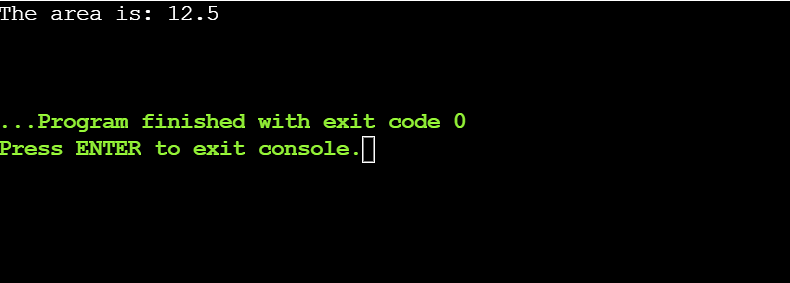
Within the instance above, it overrides the findArea() serve as of the bottom elegance by way of the findArea() of the derived elegance. When you’re making a choice to this serve as by way of the item of the derived elegance, the overriding serve as is finished.
The next comparability chart highlights the important thing variations between serve as overloading and serve as overriding in C++:
Serve as Overloading |
Serve as Overriding |
| Serve as overloading in C++ can happen without or with inheritance. |
Serve as overriding in C++ can simplest happen within the presence of inheritance. |
|
Overloaded purposes will have to have other serve as signatures i.e., the choice of parameters or the information form of parameters will have to be other. |
Overridden purposes will have to have the similar serve as signature i.e., the choice of parameters in addition to their knowledge sort will have to be he identical. |
|
It represents the compile-time polymorphism or early binding as overloading happens all over bring together time. |
It represents the run-time polymorphism or overdue binding as overriding happens all over run time. |
|
Overloading takes position inside of the similar elegance |
Overriding happens in a mother or father elegance and its kid elegance. |
|
No particular key phrase is used to overload a serve as. |
Digital key phrase within the base elegance and Override key phrase within the derived elegance can be utilized to override a serve as. |
|
Overloading is finished to procure the other habits to the similar serve as relying at the arguments handed to the purposes. |
Overriding is finished when the derived elegance serve as is anticipated to accomplish another way than the bottom elegance serve as. |
|
A category could have any choice of overloaded purposes. |
There can simplest be one overridden serve as in line with derived elegance. |
|
Execution of serve as is rapid. |
The serve as execution is relatively gradual. |
Ultimate Ideas!
On this article, you discovered crucial object-oriented programming thought referred to as means or serve as overriding in C++. You noticed how you can claim and outline a serve as within the base elegance in C++ after which override it within the kid elegance to hold out a unique capability.
You discovered vital key ideas comparable to retaining the process signature intact whilst overriding a serve as, the operating of serve as overriding, the syntax of enforcing serve as overriding in C++, and many others. Subsequent, you noticed a number of examples and use-case eventualities of serve as overriding in C++. In any case, you understood the basic variations between serve as overloading and overriding in C++.
If you wish to be told extra about different vital and key ideas in C++, you’ll be able to take a look at Simplilearn’s information on C++ for inexperienced persons.
Additionally, in case you are searching for a wealthy profession in Complete Stack Internet Building, you will have to no doubt take a look at our 9-month complete coaching program on Complete Stack Internet Building. This coaching is performed by way of business execs and can mean you can to be told trending abilities comparable to Java and its frameworks comparable to Spring, JPA, Hibernate, and many others., DevOps, Agile, HTML, CSS, and plenty of extra. Additionally, you’ll have get admission to to a capstone challenge on the finish of the path to comb up to your abilities.
If you have an interest in studying quite a lot of different abilities as smartly, you’ll be able to take a look at Simplilearn’s whole record of unfastened on-line classes.
You probably have any queries associated with this text on “Serve as Overriding in C++” or another ideas, be happy to drop a remark and our mavens gets again to you once imaginable.
Glad Finding out!
supply: www.simplilearn.com












