Image this, you’ve an inventory of 20 scholars and their marks saved in an inventory in Python within the order of lowering marks. Now, you wish to have to determine the main points of the coed who has secured the third place within the magnificence. How would you move about doing the similar?
That is the place indexing in Python involves the image. There are heaps of strategies to be had in Python that make your lifestyles so much more straightforward whilst operating with knowledge buildings reminiscent of lists, dictionaries, tuples, and so forth. One such way is the index() way in Python.
The Python index() way is helping you to find the index place of a component or an merchandise in a string of characters or an inventory of things. It spits out the bottom imaginable index of the required part within the record. In case the required merchandise does now not exist within the record, a ValueError is returned.
This information will take you thru an in-depth clarification of the way index() in Python behaves in several scenarios. And you’ll make stronger this declare with other hands-on examples.
Index() in Python
As mentioned previous, the index() in Python returns the placement of the part within the specified record or the characters within the string. It follows the similar syntax whether or not you apply it to an inventory or a string. The reason is {that a} string in Python is thought of as as an inventory of characters ranging from the index 0.
Let’s take a look at the syntax of the index() in Python.
|
>>> list_or_string_name.index(part, start_pos, end_pos) |
The parameters are as follows:
- Part: That is the record part or the string personality whose lowest index/place shall be returned.
- Start_pos: This specifies the placement of the record merchandise or the nature of the string from the place the quest starts.
- End_pos: This specifies the placement of the record part or the nature of the string from the place the quest starts.
The parameters start_pos and end_pos are non-compulsory.
Be aware: In case the part or the nature specified because the part parameter does now not exist within the iterable (record or string), then it returns a ValueError.
Additionally, the index() strategies in Python unearths and returns the bottom imaginable index of the part within the record or string. If you wish to to find the second-lowest index of the similar part, you’ll be able to to find the bottom index first, after which use this index because the start_pos parameter to start your seek from there. After which the returned worth would be the second-lowest index of the similar part.
Checklist Index in Python
As mentioned previous, if you wish to to find the placement of a component in an inventory in Python, then you’ll be able to use the index() way at the record.
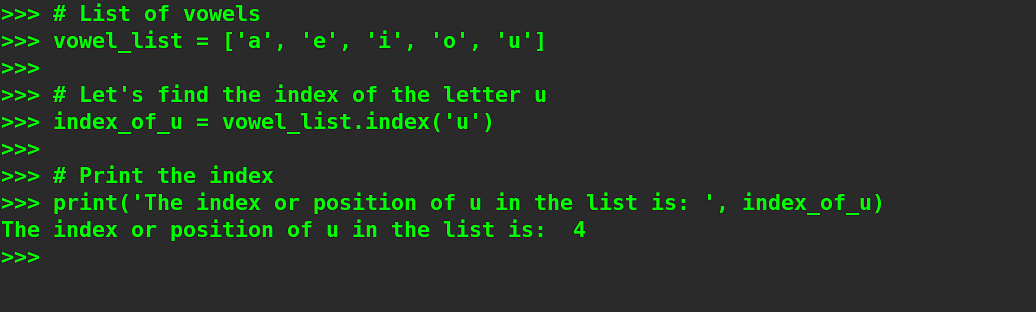
Instance 1. Discovering the Index of a Vowel in a Checklist of Vowels.
|
# Checklist of vowels # Let’s to find the index of the letter u # Print the index |
Output –
Instance 2. Discovering the Index of a String in a Checklist of Strings.
|
# Checklist of strings # Index of Jessy Pinkman # Print the outcome |
Output –

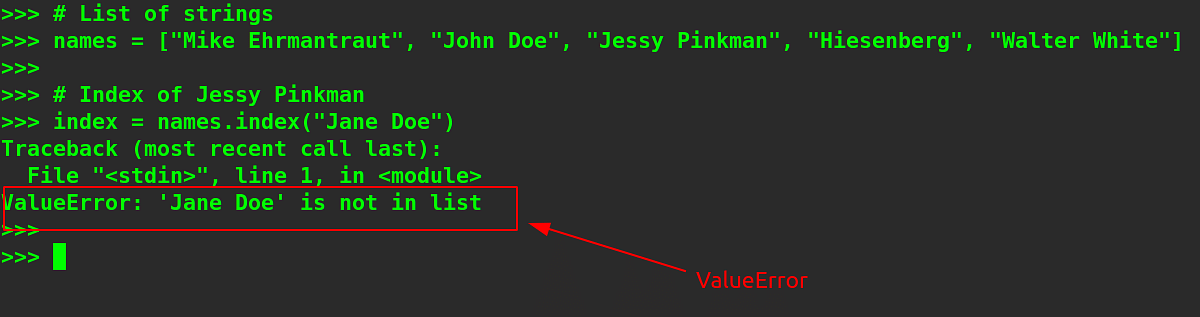
Instance 3 – Discovering an Part That Does No longer Exist.
|
# Checklist of strings # Index of Jane Doe # Print the outcome |
Output –
String Index in Python
In Python, a String is thought of as as an inventory of characters. Remember the fact that, you’ll be able to additionally observe the similar index() way on strings as neatly. The syntax of the process additionally stays the similar.
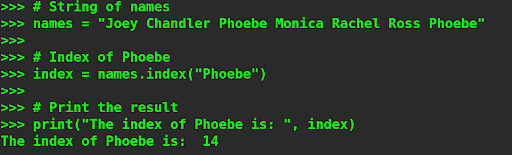
Instance 1 – Discovering a Title in a String of Names.
|
# String of names # Index of Phoebe # Print the outcome |
Output –
Rationalization –
Within the instance said above, within the string of names, the title “Phoebe” seems two times. It has used the index way at the string to search out the index of the title “Phoebe”. This returns 14 because the output. Which means that the string “Phoebe” begins from the 14th index within the string of names. Additionally, it has returned the index of the primary incidence of the title “Phoebe” within the string of the names.
Enjoying With Parameters
For the index() way in Python, you’ll be able to move 3 parameters. The primary one is the part whose index you wish to have to search out. The second one and the closing ones are the beginning and finishing indices of the string or record the place you wish to have to start and finish the quest.
Instance 1 – Operating With the Get started Parameter.
Subsequent, use the beginning parameter to specify the start place of our seek.
|
# String of names # Index of Phoebe # Print the outcome |
Output –
Rationalization –
This time the output is 40 for a similar string and the enter part. That is so as a result of you’ve discussed the beginning parameter as 15, which means that that the quest starts from the fifteenth index of the string. And the primary incidence of “Phoebe” is 14. That’s why it has returned the following incidence of the phrase “Phoebe” which is 40.
Instance 2 – Operating With the Get started and Finish Parameters
This case will specify each the beginning and the top positions in an inventory.
|
# Checklist of numbers # Index of seven # Print the outcome |
Output –
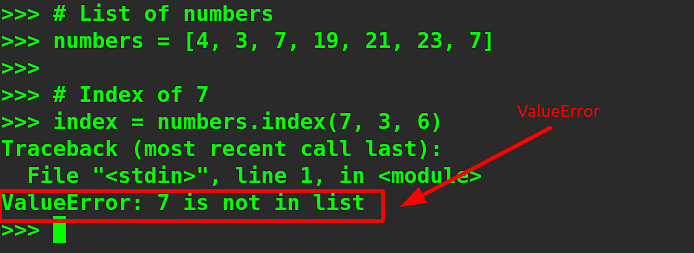
Rationalization –
It’s possible you’ll surprise, despite the fact that 7 happens two times within the record, it nonetheless outputs a ValueError. That is so as a result of you’ve discussed the beginning and finish positions as 3 and six respectively within the record. The primary incidence of seven is at index 2 and the closing is at index 6. Please word that while you specify an finishing index, it in fact searches as much as the index (end_pos – 1). On this case, it searches as much as the fifth index should you specify the end_pos to be 6. And between indices 3 and 5, the part 7 does now not happen even as soon as, therefore it outputs the ValueError.
Conclusion
On this article, you explored the index in Python and went thru some sensible examples that might let you achieve hands-on enjoy at the subject. It began with a elementary dialogue of the index way, after which mentioned the syntax of the process, along side the imaginable parameters.
It additionally noticed how the similar way can also be carried out on each lists and strings thru sensible examples and a couple of situations. After all, you explored how you can use the opposite two parameters to restrict the quest.
Have any questions for us? Point out them as feedback beneath, and our professionals gets again to you once imaginable!
supply: www.simplilearn.com












